Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 5 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 5
Directions: Read the following passage carefully:
Theft is a general term embracing a wide variety of misconduct by which a person is improperly deprived of his property. Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any property out of the possession of another person, moves that property for such taking, is said to commit theft.
The purpose of theft law is to promote security of property by threatening aggressors with punishment. Property security is valued as part of the individual's enjoyment of his belongings and because the community wishes to encourage saving and economic planning, which would be jeopardized if accumulated property could be plundered with impunity. Another function of the law of theft is to divert the powerful acquisitive instinct from non-productive preying on others to productive activity.
One problem that dogs the law of theft, as will be seen below, is that in a commercial society no clear line can be drawn between greedy antisocial acquisitive behavior on the one hand and, on the other hand, aggressive selling, advertising, and other entrepreneurial activity that is highly regarded or at least commonly tolerated. Here two important principles of constitutional and criminal law come into play to restrict the scope of the law of theft. A criminal law must not be so comprehensive as to jeopardize the ordinary behavior of decent citizens.
Nor may a criminal law be so vague that it fails to warn the citizen what is forbidden and leaves to the discretion of enforcement officers or judges whether certain behavior should be punishable. The tension between these principles, and the impulse to penalize all egregious greed, account for the fact that theft law inevitably falls short of penalizing all rascality. Whoever intending to take dishonestly with an intention to cause wrongful loss to another or wrongful gain to himself any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person's consent, moves that property in order to such taking is said to commit theft.
At the same time—such are the refractory problems of legislative drafting—it is impossible, even with the most painstaking draftsmanship, to avoid overpenalizing in some cases. For example, obviously trivial peculations such as using an employer's stationery for writing personal notes quite clearly fall within theft law; yet it has proved impossible to articulate exceptions that will exclude this and a myriad of other trivial violations. Such things remain, therefore, within the province of prosecutorial and judicial discretion.
Q. Tia, Soham's wedding planner went to Soham's office to discuss his wedding plans. Since Soham was not in his office, Tia waited in his cabin. Tia had few card designs and few samples of return gift with her. When Soham didn't turn up, Tia collected all the samples and cards and took along with her. As she was collecting the sample return gifts, Tia also took a stone resembling a return gift from his table. Since the stone happened to be a valuable one, Soham filed a complaint and it was traced in Tia's office.
Directions: Read the following passage carefully:
Theft is a general term embracing a wide variety of misconduct by which a person is improperly deprived of his property. Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any property out of the possession of another person, moves that property for such taking, is said to commit theft.
The purpose of theft law is to promote security of property by threatening aggressors with punishment. Property security is valued as part of the individual's enjoyment of his belongings and because the community wishes to encourage saving and economic planning, which would be jeopardized if accumulated property could be plundered with impunity. Another function of the law of theft is to divert the powerful acquisitive instinct from non-productive preying on others to productive activity.
One problem that dogs the law of theft, as will be seen below, is that in a commercial society no clear line can be drawn between greedy antisocial acquisitive behavior on the one hand and, on the other hand, aggressive selling, advertising, and other entrepreneurial activity that is highly regarded or at least commonly tolerated. Here two important principles of constitutional and criminal law come into play to restrict the scope of the law of theft. A criminal law must not be so comprehensive as to jeopardize the ordinary behavior of decent citizens.
Nor may a criminal law be so vague that it fails to warn the citizen what is forbidden and leaves to the discretion of enforcement officers or judges whether certain behavior should be punishable. The tension between these principles, and the impulse to penalize all egregious greed, account for the fact that theft law inevitably falls short of penalizing all rascality. Whoever intending to take dishonestly with an intention to cause wrongful loss to another or wrongful gain to himself any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person's consent, moves that property in order to such taking is said to commit theft.
At the same time—such are the refractory problems of legislative drafting—it is impossible, even with the most painstaking draftsmanship, to avoid overpenalizing in some cases. For example, obviously trivial peculations such as using an employer's stationery for writing personal notes quite clearly fall within theft law; yet it has proved impossible to articulate exceptions that will exclude this and a myriad of other trivial violations. Such things remain, therefore, within the province of prosecutorial and judicial discretion.
Q. Kabir owed some money to Sia. Sia removed his horse, which was grazing by the side of a river, and kept it tied in her own farm. When Kabir asked her to release the horse, Sia told him that she would do so when the money was paid to her. Kabir filed a case against Sia.
Directions: Read the following passage carefully:
Theft is a general term embracing a wide variety of misconduct by which a person is improperly deprived of his property. Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any property out of the possession of another person, moves that property for such taking, is said to commit theft.
The purpose of theft law is to promote security of property by threatening aggressors with punishment. Property security is valued as part of the individual's enjoyment of his belongings and because the community wishes to encourage saving and economic planning, which would be jeopardized if accumulated property could be plundered with impunity. Another function of the law of theft is to divert the powerful acquisitive instinct from non-productive preying on others to productive activity.
One problem that dogs the law of theft, as will be seen below, is that in a commercial society no clear line can be drawn between greedy antisocial acquisitive behavior on the one hand and, on the other hand, aggressive selling, advertising, and other entrepreneurial activity that is highly regarded or at least commonly tolerated. Here two important principles of constitutional and criminal law come into play to restrict the scope of the law of theft. A criminal law must not be so comprehensive as to jeopardize the ordinary behavior of decent citizens.
Nor may a criminal law be so vague that it fails to warn the citizen what is forbidden and leaves to the discretion of enforcement officers or judges whether certain behavior should be punishable. The tension between these principles, and the impulse to penalize all egregious greed, account for the fact that theft law inevitably falls short of penalizing all rascality. Whoever intending to take dishonestly with an intention to cause wrongful loss to another or wrongful gain to himself any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person's consent, moves that property in order to such taking is said to commit theft.
At the same time—such are the refractory problems of legislative drafting—it is impossible, even with the most painstaking draftsmanship, to avoid overpenalizing in some cases. For example, obviously trivial peculations such as using an employer's stationery for writing personal notes quite clearly fall within theft law; yet it has proved impossible to articulate exceptions that will exclude this and a myriad of other trivial violations. Such things remain, therefore, within the province of prosecutorial and judicial discretion.
Q. Ajay handed over his mother's jewellery to his girlfriend, Jaya, for safekeeping. His girlfriend was in a need of money as she was planning a surprise for Ajay's birthday. Jaya sold the jewellery to Mohan, though she was not authorised to do so. Ajay filed a suit against Jaya.
Directions: Read the following passage carefully:
Theft is a general term embracing a wide variety of misconduct by which a person is improperly deprived of his property. Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any property out of the possession of another person, moves that property for such taking, is said to commit theft.
The purpose of theft law is to promote security of property by threatening aggressors with punishment. Property security is valued as part of the individual's enjoyment of his belongings and because the community wishes to encourage saving and economic planning, which would be jeopardized if accumulated property could be plundered with impunity. Another function of the law of theft is to divert the powerful acquisitive instinct from non-productive preying on others to productive activity.
One problem that dogs the law of theft, as will be seen below, is that in a commercial society no clear line can be drawn between greedy antisocial acquisitive behavior on the one hand and, on the other hand, aggressive selling, advertising, and other entrepreneurial activity that is highly regarded or at least commonly tolerated. Here two important principles of constitutional and criminal law come into play to restrict the scope of the law of theft. A criminal law must not be so comprehensive as to jeopardize the ordinary behavior of decent citizens.
Nor may a criminal law be so vague that it fails to warn the citizen what is forbidden and leaves to the discretion of enforcement officers or judges whether certain behavior should be punishable. The tension between these principles, and the impulse to penalize all egregious greed, account for the fact that theft law inevitably falls short of penalizing all rascality. Whoever intending to take dishonestly with an intention to cause wrongful loss to another or wrongful gain to himself any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person's consent, moves that property in order to such taking is said to commit theft.
At the same time—such are the refractory problems of legislative drafting—it is impossible, even with the most painstaking draftsmanship, to avoid overpenalizing in some cases. For example, obviously trivial peculations such as using an employer's stationery for writing personal notes quite clearly fall within theft law; yet it has proved impossible to articulate exceptions that will exclude this and a myriad of other trivial violations. Such things remain, therefore, within the province of prosecutorial and judicial discretion.
Q. Adi finds a painting at Delhi railway station, not knowing to whom it belongs; afterwards he discovers that it belongs to Rima and appropriates it to his own use. Rima sued Adi under the court of law.
Directions: Read the following passage carefully:
Theft is a general term embracing a wide variety of misconduct by which a person is improperly deprived of his property. Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any property out of the possession of another person, moves that property for such taking, is said to commit theft.
The purpose of theft law is to promote security of property by threatening aggressors with punishment. Property security is valued as part of the individual's enjoyment of his belongings and because the community wishes to encourage saving and economic planning, which would be jeopardized if accumulated property could be plundered with impunity. Another function of the law of theft is to divert the powerful acquisitive instinct from non-productive preying on others to productive activity.
One problem that dogs the law of theft, as will be seen below, is that in a commercial society no clear line can be drawn between greedy antisocial acquisitive behavior on the one hand and, on the other hand, aggressive selling, advertising, and other entrepreneurial activity that is highly regarded or at least commonly tolerated. Here two important principles of constitutional and criminal law come into play to restrict the scope of the law of theft. A criminal law must not be so comprehensive as to jeopardize the ordinary behavior of decent citizens.
Nor may a criminal law be so vague that it fails to warn the citizen what is forbidden and leaves to the discretion of enforcement officers or judges whether certain behavior should be punishable. The tension between these principles, and the impulse to penalize all egregious greed, account for the fact that theft law inevitably falls short of penalizing all rascality. Whoever intending to take dishonestly with an intention to cause wrongful loss to another or wrongful gain to himself any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person's consent, moves that property in order to such taking is said to commit theft.
At the same time—such are the refractory problems of legislative drafting—it is impossible, even with the most painstaking draftsmanship, to avoid overpenalizing in some cases. For example, obviously trivial peculations such as using an employer's stationery for writing personal notes quite clearly fall within theft law; yet it has proved impossible to articulate exceptions that will exclude this and a myriad of other trivial violations. Such things remain, therefore, within the province of prosecutorial and judicial discretion.
Q. Bhola went to buy a watch to be gifted to his son with a view to find a watch similar to the one he owns. He selected the watch but when he saw the price tag, he gave it up. But meanwhile, he inadvertently took the valuable watch from the shop and left his less valuable watch in the casket of the valuable watch. Nobody in the shop noticed it and he also discovered it only after reaching home.
According to which article of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights are rights such as the right to life, freedom of thought, prohibition of slavery, etc. said to be non-derogable?
Directions: Consider the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R), and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): Writ jurisdiction of the Supreme Court is exclusive.
Reason (R): The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction in terms of issuing writs, i.e. a citizen can go directly to the Supreme Court and not by way of appeal.
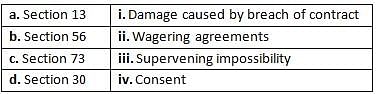
An agreement not supported by consideration is called which of the following?
Directions: Consider the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R), and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): In an adversarial system, the parties in a legal proceeding develop their own theory of the case and gather evidence to support their claims.
Reason (R): In an adversarial system, cross examination is an effective way to test the credibility of the witnesses presented.
Which of the following is/are the function(s) of Central authority?
The Law Society of _______ determines fitness of character for admission.
Which of the following doctrines requires that only the parties to the contract can enforce it?
'You must not use a steam hammer to crack a nut if a nut cracker would do.' This statement refers to which doctrine of Administrative Law?
Which case gave primacy to the Executive in making judicial appointments?
The concept of Public Interest Litigation, which has become quite popular in India, originated in
Which of the following US states have unified bars?
Which of the following functions are performed by the Bar Council of India?
Directions: The question contains two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R). Examine whether the statements are correct and related to each other with the help of the codes given below:
Assertion (A): Directive principles of state policy are not enforceable in a court of law.
Reason (R): Directive principles are only moral obligations.
In the Vedic age in India, which of the following specialised tribunals dealt with disputes related to castes?
Appointments of persons (other than district judges) to the judicial service of a State are made by the Governor of the State after consulting
The 'Power of Judicial Review' and 'Independence of the Judiciary' principles of the Indian Constitution are borrowed from the ________ Constitution.
A promises, for no consideration, to give to B Rs. 1000. The agreement is
Directions: The following question consists of a legal proposition/principle (hereinafter referred to as 'principle') and facts. This principle has to be applied to the given facts to arrive at the most reasonable conclusion. Such principle may or may not be true in the real sense, yet you have to conclusively assume it to be true for the purpose of the question. In other words, in answering the question, you must not rely on any principle except the principle that is given herein below for the given question. Further, you must not assume any facts other than the facts stated in the question. The objective of this question is to test your interest towards study of law, research aptitude and problem solving ability even if the 'most reasonable conclusion' arrived at may be unacceptable for any other reason. It is not the object of this question to test your knowledge of law.
Principle: A person is responsible for his own act of omission and commission, but in certain cases a person is liable for the act of others. The wrongful act of others must be done within the course of employment. This is known as vicarious liability.
Facts: A careless petrol lorry driver during his working hours was smoking whilst transferring petrol from a tanker to a tank. The employee was carrying out an authorised task (transferring petrol) in an unauthorised manner (whilst smoking) which results into explosion.
Q. Is the employer liable for the act of the employee?
The police cannot investigate ________ without the order of a Magistrate.
A frustrated judge in an English court finally asked a barrister after witnesses had produced conflicting accounts,' Am I never to hear the truth? 'No, my lord, merely the evidence', replied counsel. To which judicial system does this judge belong?
Which of the following is the correct chronological order of the following Human Rights documents?
(a) International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
(b) Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women
(c) Universal Declaration of Human Rights
(d) Convention on the Rights of the Child
|
8 docs|148 tests
|