Physics: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 2
A wire placed along the north-south direction carries a current of 8 A from south to north. Find the magnetic field due to a 1 cm piece of wire at a point 200 cm north-east from the piece.
Three charges –q, Q and –q are placed in a straight line maintaining equal distance from each other. What should be the ratio q/Q so that the net electric potential of the system is zero?
Two resistors are connected in parallel, whose resistance values are in the ratio 3:1. Find the ratio of power dissipated.
Which among the following can be used to analyze circuits?
Two point charges +4q and +q are kept at a distance of 30 cm from each other. At which point between them, the field intensity will be equal to zero?
If a non-polar substance is placed in an electric field, what will happen?
What is the net electrostatic field in the interior of a conductor?
A set up is such that there are three similar resistors, each of 20 ohms resistance. Two of them are connected in parallel, and this combination is connected in series with the third one. The maximum power that can be consumed by each resistor is 30 W. Then, what is the maximum power that can be consumed by the combination of all three resistors?
Give the SI unit of magnetic permeability of free space.
Identify the expression for ampere’s circuital law from the following?
What torque acts on a 50 turn coil of 200 cm2 area carrying a current of 20 A held with its axis at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of 0.2T?
State the rule that is used to find the direction of field acting at a point near a current-carrying straight conductor.
What is the maximum torque on a rectangular coil of area 4 cm × 80 cm of 400 turns, when carrying a current of 103 A in a magnetic field of 0.2 T?
How is the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor related to the surface charge density?
Identify the factor on which the torque on a planar current loop does not depend.
Which of the following is not a point of similarity between Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law.
What is the total work done on moving a test charge on an equipotential surface?
A long straight wire of radius x carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic field at x/4 and 8x.
‘X’ is the phenomenon of making a region free from any electric field. Identify X.
|
8 docs|148 tests
|



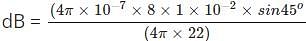

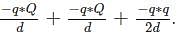 But the total energy of the system is zero. So, -qQ - qQ + q2/2 = 0 hat means q = 4Q, i.e. q/Q = 4.
But the total energy of the system is zero. So, -qQ - qQ + q2/2 = 0 hat means q = 4Q, i.e. q/Q = 4.
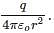 Let the electric field intensity will be zero at a distance of x cm from +4q charge, so the fields due to the two charges will balance each other at that point. Therefore
Let the electric field intensity will be zero at a distance of x cm from +4q charge, so the fields due to the two charges will balance each other at that point. Therefore 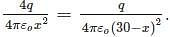 Solving this we get x=20cm. Therefore the point will be 20cm away from the +4q charge.
Solving this we get x=20cm. Therefore the point will be 20cm away from the +4q charge.