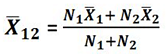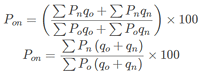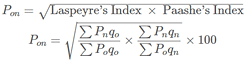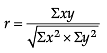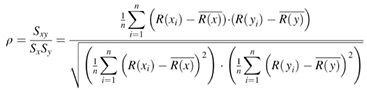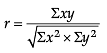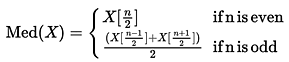Test: Use of Statistical Tools- Match Based Type Questions - Commerce MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Economics Class 11 - Test: Use of Statistical Tools- Match Based Type Questions
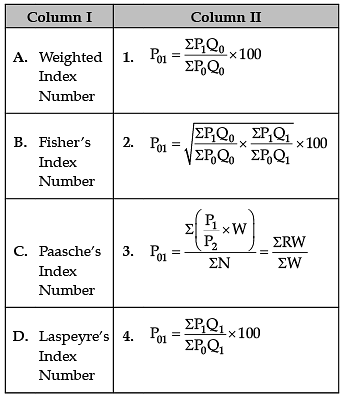
Identify the correct pair of terms with their formula from the following Columns I and II:
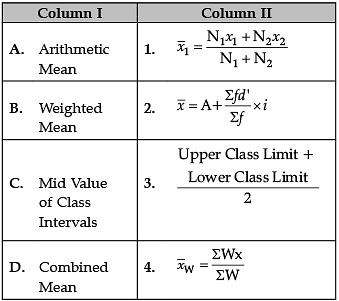

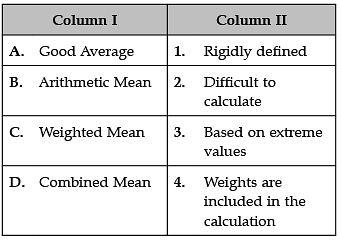
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
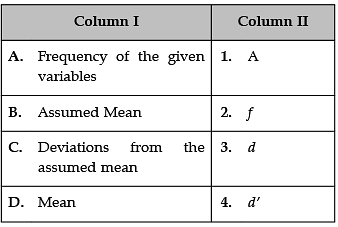
Identify the correct pair of terms with their common symbols from the following Columns I and II:

Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
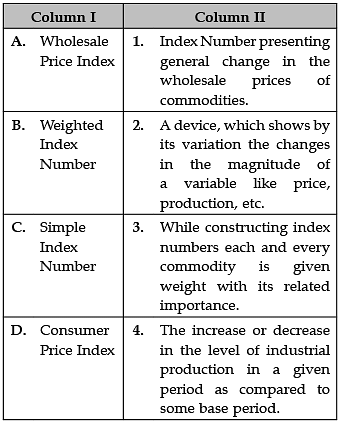
Identify the correct pair of terms and definitions from the following Columns I and II:
Identify the correct pair of terms with their definition from the following Columns I and II:
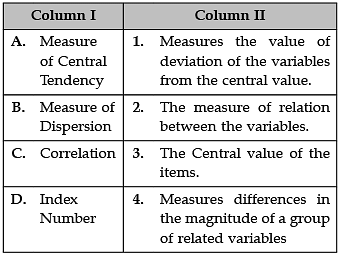
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
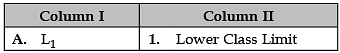

Identify the correct pair of terms and definitions from the following Columns I and II:
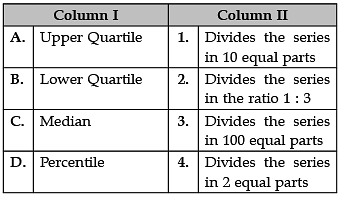
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
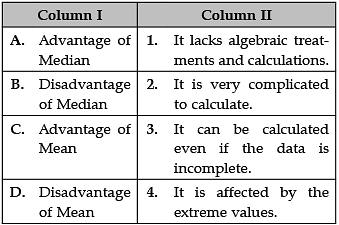
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
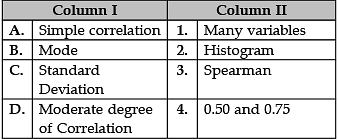
Identify the correct pair of terms and definitions from the following Columns I and II:
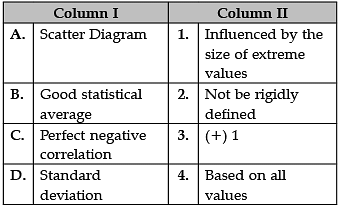
Identify the correct pair of terms with their formulae from the following Columns I and II:
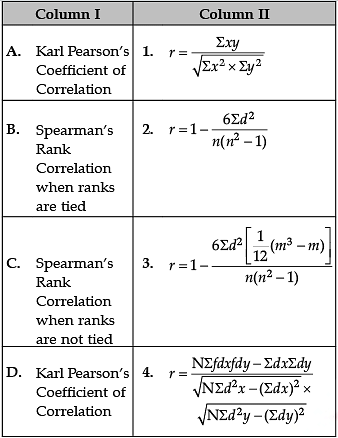
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
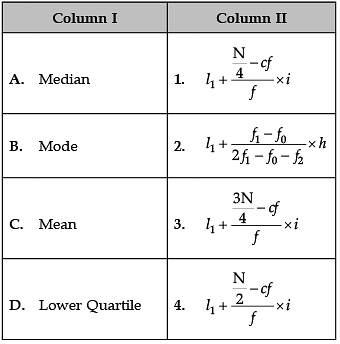
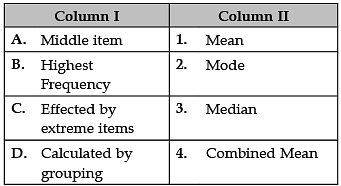
Identify the correct pair of terms and definitions from the following Columns I and II:
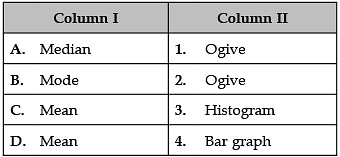
Identify the correct pair of terms with their definition from the following Columns I and II:
|
58 videos|215 docs|44 tests
|