IBPS Clerk Prelims Mock Test - 1 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test IBPS Clerk Mock Test Series & Past Year Papers 2024 - IBPS Clerk Prelims Mock Test - 1
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Which of the following is the synonym of the word INCUR used in the passage?
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Four words are given in bold. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct.
Q. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Read the sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The number of that part is the answer.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Which of the following statements are not true based on the passage given.
I. Scientific Reports published that if deforestation continues at its current rate in the next 20 – 30 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity.
II. Deforestation, clearance or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to forest use
III. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute.
IV. Net change can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Which of the following are not the causes of deforestation according to the passage?
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Which organisation defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses?
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given. Certain words/phrases have been given in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Deforestation, clearance, clear cutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Belgium, are destroyed every year, on average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a given period. Net change, therefore, can be positive or negative, depending on whether gains exceed losses, or vice versa.
The removal of trees without sufficient reforestation has resulted in habitat damage, biodiversity loss, and aridity. Deforestation causes extinction, changes to climatic conditions, desertification, and displacement of populations, as observed by current conditions and in the past through the fossil record. Deforestation also has adverse impacts on biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, increasing negative feedback cycles contributing to global warming. Global warming also puts increased (A)/pressure on communities who seek food security (B) / by clearing forests for agricultural use (C)/ and reduce arable land more generally(D)/No error (E). Deforested regions typically incur significant other environmental effects such as adverse soil erosion and degradation into wasteland.
The resilience of human food systems and their capacity to adapt to future change depends on that very biodiversity – including dry land-adapted shrub and tree species that help combat desertification, forest-dwelling insects, bats and bird species that pollinate crops, trees with extensive root systems in mountain ecosystems that prevent soil erosion, and mangrove species that provide resilience against flooding in coastal areas. With climate change capturing (a) the risks to food systems, the role of forests in exacerbating (b) and storing carbon and increasing (c) climate change is of ever mitigating (d) importance for the agricultural sector.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports if deforestation continues in current rate in the next 20 – 40 years, it can trigger a full or almost full extinction of humanity. To avoid it humanity should pass from a civilization dominated by the economy to "cultural society" that "privileges the interest of the ecosystem above the individual interest of its components, but eventually in accordance with the overall communal interest".
Q. Which of the following defines all forest gains in the passage?
In the questions below, a table is given with two columns. In Column I, the first part of the sentence is given whereas in Column II second part of the sentence is given. Find the correct possible combination sentence from the options given.
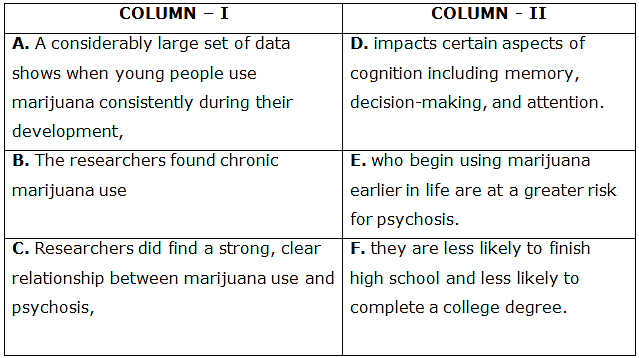
In the questions below, a table is given with two columns. In Column I, the first part of the sentence is given whereas in Column II second part of the sentence is given. Find the correct possible combination sentence from the options given.
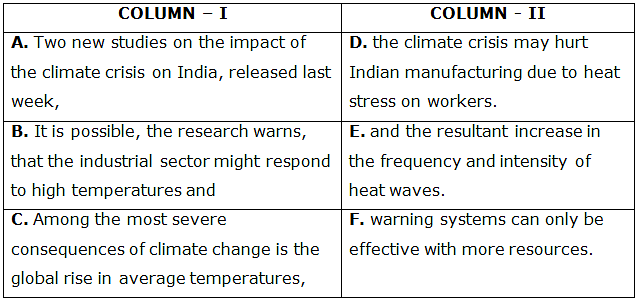
In the questions below, a table is given with two columns. In Column I, the first part of the sentence is given whereas in Column II second part of the sentence is given. Find the correct possible combination sentence from the options given.

In the questions below, a table is given with two columns. In Column I, the first part of the sentence is given whereas in Column II second part of the sentence is given. Find the correct possible combination sentence from the options given.

Each question below has one blank, which is indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the most suitable option indicating the words that can be used to fill up the blank in the sentence to make it meaningfully complete.
In their chase, the hosts were off to a flying start as Guptill and Nicholls shared a 106-run stand before Chahal _______ Guptill with a beautiful delivery,
Each question below has one blank, which is indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the most suitable option indicating the words that can be used to fill up the blank in the sentence to make it meaningfully complete.
The road from National Highway-37 point to Kalinagar, Part-III's Tukergram-Bokrihawor dyke in Hailakandi district has reportedly been in a _______ condition for the last many months.
Each question below has one blank, which is indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the most suitable option indicating the words that can be used to fill up the blank in the sentence to make it meaningfully complete.
The Consulate General of India here has _________ a new drive aimed at upgrading skills and roles of blue-collar workers to the new normal.
Each question below has one blank, which is indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the most suitable option indicating the words that can be used to fill up the blank in the sentence to make it meaningfully complete.
INS Talwar was the ‘On Scene Coordinator' off Gujarat coast and assisted Support Station 3 (SS3) and Drill Ship SagarBhushan, which are now being safely _______ to Mumbai by ONGC support vessels.
A sentence given below divided into five parts with one part of the sentence not related to central theme of the sentence. You have to choose correct rearrangement of sentence with elimination of the odd one from the sentence in the options given.
saying it was one-sided and packed with false assertions (A)/ The Indian government has slammed a debate (B)/ in London issued a statement immediately after the debate(C)/ and safety of farmer’s protestors in India (D)/ held in the House of Commons on press freedom (E)
A sentence given below divided into five parts with one part of the sentence not related to central theme of the sentence. You have to choose correct rearrangement of sentence with elimination of the odd one from the sentence in the options given.
promising a monthly honorarium of Rs1,500 to women (A)/ heads of families and six domestic LPG cylinders (B)/ Chief Minister Edappadi K Palaniswami on Monday stepped on the populist gas,(C)/ this promise from the yet-to-be-released AIADMK manifesto.(D)/ per year free to every household in Tamil Nadu (E)
A sentence given below divided into five parts with one part of the sentence not related to central theme of the sentence. You have to choose correct rearrangement of sentence with elimination of the odd one from the sentence in the options given.
Darekar made the demand in the legislative council on Monday (A)/Deshmukh said the guilty will not be spared (B)/ after state home minister Anil Deshmukh read out a statement (C)/ for murder on the complaint of Hiran’s wife Vimla(D)/ that the ATS had registered an FIR (E)
A sentence given below divided into five parts with one part of the sentence not related to central theme of the sentence. You have to choose correct rearrangement of sentence with elimination of the odd one from the sentence in the options given.
a teacher from Hindi medium school, used Google forms to reach (A)/ 79% students said they were dissatisfied with the decision (B)/ While the state government has been stern (C)/ offline in April in the current format, (D)/ on its decision to conduct SSC and HSC exams. (E)
A sentence given below divided into five parts with one part of the sentence not related to central theme of the sentence. You have to choose correct rearrangement of sentence with elimination of the odd one from the sentence in the options given.
based on complaints about sub-stranded range performance (A)/ temporarily suspend subsidy on nexon electronic vehicles, (B)/ the company has claimed the government took the extreme step (C)/ Tata Motors has moved Delhi High Court (D)/ challenging the AAP government’s decision to (E)
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. What is the main reason to make an amendment in the law?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. What changes will come after the bill has passed?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. Who can be benefitted from the deposit insurance scheme?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. What can we infer from the passage?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. Consider the following statements and answer the question.
A. the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs. 5 lakh.
B. The amendment is brought by the suggestion of RBI.
C. The amendment is made to ease the burden of the depositors.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. Consider the following statements and choose the correct option.
A. the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakh.
B. The increase is never seen in Indian history.
C. DICGC is a subsidiary of the Indian govt.
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. Which of the following is a synonym of the word curtailment?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and select the best answer to each question out of the given five alternatives.
In a bid to ensure timely support to depositors of stressed banks, the government may bring amendment to DICGC Act in the monsoon session with the objective to provide account holders easy and time-bound access to funds to the extent of the deposit insurance cover. Last year, the government raised insurance cover on deposit five-folds to Rs 5 lakh with a view to provide support to depositors of ailing lenders like Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank. Following the collapse of PMC Bank, Yes Bank and Lakshmi Vilas Bank NSE 4.79 % too came under stress leading to restructuring by the regulator and the government.
The amendment to the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961 is the budget announcement made by the Finance Minister and the Bill is almost ready, sources said. It is expected that the Bill will be tabled in the upcoming monsoon session after being vetted by the Union Cabinet, sources added. Once the Bill becomes the law, it will provide immediate relief to thousands of depositors who had their money parked in stressed lenders such as PMC Bank and other small cooperative banks.
As per the current provisions, the deposit insurance of up to Rs 5 lakh comes into play when the licence of a bank is cancelled and liquidation process starts. DICGC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India, provides insurance cover on bank deposits. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Budget speech in February said the government had approved an increase in the Deposit Insurance cover from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh for bank customers last year. It could not be presented in the Budget session due to curtailment of the last session following the spread of the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic.
It is to be noted that the enhanced deposit insurance cover of Rs 5 lakh is effective from February 4, 2020. The increase was done after a gap of 27 years as it was static since 1993. The cover is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI. With increased insurance cover, the banks are paying a higher premium of 12 paise against 10 paise per Rs 100 deposited without any additional burden on account holders. The deposit insurance scheme covers all banks operating in India, including private sector, cooperative, and even branches of foreign banks. There are some exemptions such as deposits of foreign governments, deposits of central and state governments, and inter-bank deposits.
It can be recalled that way back in 2009, the Raghuram Rajan committee on financial sector reforms had recommended strengthening the capacity of the DICGC, a more explicit system of prompt, corrective action, and making deposit insurance premia more risk-based.
Q. Which of the following is an antonym of the word 'ailing'?
In the following paragraph, there is a set of four highlighted words against each number indicated in Underline in the beginning of the sentences. One of the given words in each set may or may not fit into the statement. Choose the word which is not suitable in the context of the paragraph. If all the four words are correct and feasible, choose (e) i.e. “No error” as your answer.
(21) The much-awaited vehicle scrappage policy announced by the Transport Ministry, coming after the move for a green tax on adulterated and polluting automobiles, promises economic benefits, a cleaner environment and thousands of jobs. (22) Although it will take until April 1, 2022 for vehicles belonging to the government and the public sector to be scrapped, another year thereafter to intensify junk heavy commercial vehicles through mandatory fitness checks, and finally other vehicles by 2024, it is a constructive road map. (23) It will be no easy task, however, to put in place a vague system of automated fitness checking centers with help from States to assess whether commercial and private vehicles are roadworthy after 15 and 20 years, respectively, as the policy envisages. Equally important, enforcement will be key to get them scrapped once they are found unfit for use and to stop them from moving to smaller towns. (24) States must also come on board to provide road tax and registration concessions, while the automobile industry is accepted to sweeten the deal with genuine discounts on new vehicles. (25) Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari, who has had limited success with enforcement of the amended Motor Vehicles Act of 2019 because States are not eternally on board, has the difficult task of ensuring that the scrappage plan gets their support, and the backing of manufacturers who stand to benefit from a spurt in demand. Heavy commercial vehicles, which contribute disproportionately to pollution — 1.7 million lack fitness certificates — pose the biggest challenge. (26) Many of these cannot be replaced quickly in the absent of financial arrangements for small operators, who have opposed the new measures.
Q. Which of the following word is incorrect in the statement marked (21)?
In the following paragraph, there is a set of four highlighted words against each number indicated in Underline in the beginning of the sentences. One of the given words in each set may or may not fit into the statement. Choose the word which is not suitable in the context of the paragraph. If all the four words are correct and feasible, choose (e) i.e. “No error” as your answer.
(21) The much-awaited vehicle scrappage policy announced by the Transport Ministry, coming after the move for a green tax on adulterated and polluting automobiles, promises economic benefits, a cleaner environment and thousands of jobs. (22) Although it will take until April 1, 2022 for vehicles belonging to the government and the public sector to be scrapped, another year thereafter to intensify junk heavy commercial vehicles through mandatory fitness checks, and finally other vehicles by 2024, it is a constructive road map. (23) It will be no easy task, however, to put in place a vague system of automated fitness checking centers with help from States to assess whether commercial and private vehicles are roadworthy after 15 and 20 years, respectively, as the policy envisages. Equally important, enforcement will be key to get them scrapped once they are found unfit for use and to stop them from moving to smaller towns. (24) States must also come on board to provide road tax and registration concessions, while the automobile industry is accepted to sweeten the deal with genuine discounts on new vehicles. (25) Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari, who has had limited success with enforcement of the amended Motor Vehicles Act of 2019 because States are not eternally on board, has the difficult task of ensuring that the scrappage plan gets their support, and the backing of manufacturers who stand to benefit from a spurt in demand. Heavy commercial vehicles, which contribute disproportionately to pollution — 1.7 million lack fitness certificates — pose the biggest challenge. (26) Many of these cannot be replaced quickly in the absent of financial arrangements for small operators, who have opposed the new measures.
Q. Which of the following word is incorrect in the statement marked (22)?
|
20 docs|63 tests
|
|
20 docs|63 tests
|

















