Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 1 (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 1 (Old NCERT)
Cucurbits and coconuts are examples of _______
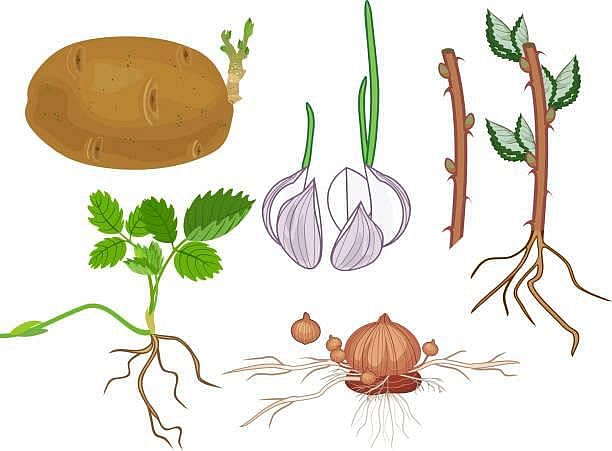
Which plant can propagate vegetatively by leaf?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What are the two main pre fertilization events?
Chances of survival are more for ______ animals.
What is the period from birth to natural death of an organism known as?
The degenerative and irreversible changes in the organism is known as_______.
What is the thick wall developed on a fruit called?
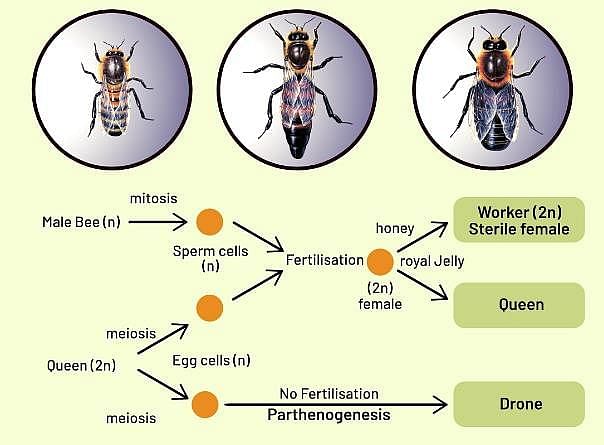
Which of the following is developed by parthenogenesis:
What is the period of growth known as in plants?
Senescence in most of the animals is NOT caused by _____.
Which of the following is NOT correct about artificial means of vegetative propagation?
Identify the organism and type of reproduction in figure below.
A flower having both male and female reproductive parts are termed as______.
The chances of survival of a young one is greater in ___________ organism.
________ is retained throughout generations in parthenogenesis.
In which of the following does syngamy occur inside?
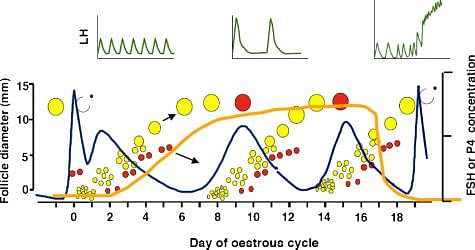
In non-primate mammals like cows, sheep, rats, dogs etc., such cyclical changes during reproduction are called?
Which plant is the “terror of Bengal”?
Sexual reproduction is better mode of reproduction because offspring _____.
Appearance of vegetative propagules from the nodes of plants such as sugarcane & ginger is mainly because
Choose the correct statement amongst the following:
Which of the following situations correctly describe the similarity between an angiosperm egg & a human egg?
(a) Eggs of both are formed only once in a lifetime.
(b) Both the angiosperm egg & human egg are stationary.
(c) Both the angiosperm egg & human egg are motile transported.
(d) Syngamy in both results in the formation of zygote.
Arrange the following in order of their occurrence in plants.
Which of the following is a post fertilization event in flowering plants?