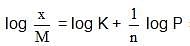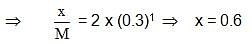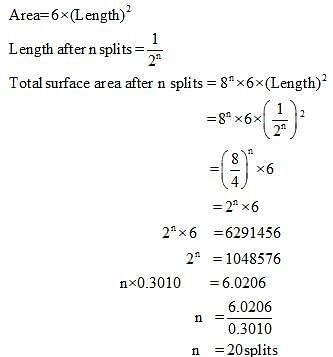P. Bahadur Test: Surface Chemistry (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - P. Bahadur Test: Surface Chemistry (Old NCERT)
When a graph is plotted between log x/m and log p, it is straight line With an angle 45° and intercept 0.3010 on y-axis. If initial pressure is 0.3 atm, what will be the amount of gas adsorbed per gm of adsorbent :
Which of the following statements about physical adsorption is not correct ?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Following is the variation of physical adsorption with temperature:
Finally divided catalyst has greater surface area and has greater catalytic activity then the compact solid. If a total surface area of 6291456 cm is required for adsorption of gaseous reaction in a catalysed reaction, then how many splits should be made of cube exactly 1 cm in length.
Which of the following is not characteristic of chemisorption?
A colloidal solution can be purified following the method of
Gold number of a lyophilic sol is such property that:
100 mL of a colloidal solution is completely precipitated by addition of 5 mL of 1 M Nacl solution . Calculate the coagulation value of Nacl .
Some type of gels like gelatin loose water slowly. The process is known as :
During the adsorption of Krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature
Size of colloidal particles may range from
Gold number of haemoglobin is 0.03. Hence, 100 mL of gold sol will require haemoglobin so that gold is not coagulated by 10 mL of 10% NaCl solution:
Which one of the following statements is correct:
What can adsorb larger volume of hydrogen gas :
Statement-1 : All colloidal dispersions give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling pointelevation.
Statement-2 : Tydall effect is due to scattering of light from the surface of colloidal particles.
Statement-1 : The Brownian movement is due to the bombardment of collodial particles by the molecules of dispersion medium which are in the constant motion like molecules in a gas.
Statement-2 :Brownian movement provides a visible proof of the random kinetic motion of molecules in a liquid.
Statement-1: In the coagulation of negatively charged arsenic sulphide soil, the coagulating power decreases in the order, Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+.
Statement-2 : Generally greater the valence of coagulating ion, the greater is its power of coagulation.
Assertion: Isoelectric point is pHpH at which colloidal can move towards either of electrode.
Reason: At isoelectric point coolidal particles becomes electrically netural .
|
108 videos|287 docs|123 tests
|