Test: Globalization- Case Based Type Questions - Humanities/Arts MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test Political Science Class 12 - Test: Globalization- Case Based Type Questions
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
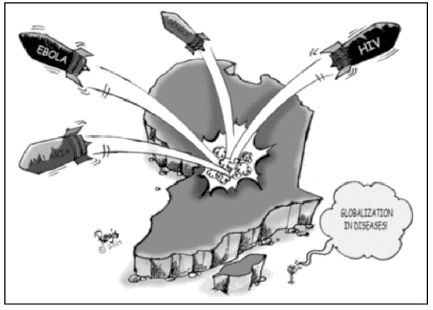
Q. Who identified the four basic aspects of globalization?

Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
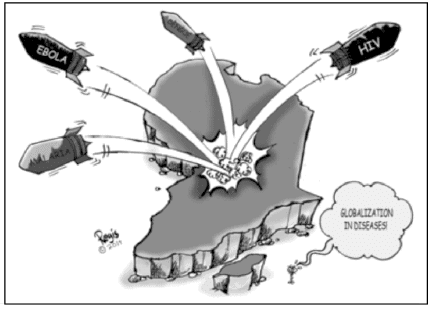
Q. Why is Africa featured in the above picture?

Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
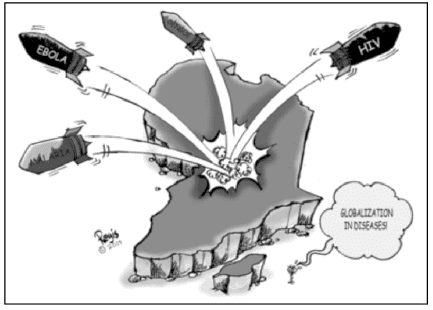
Q. What is depicted in the picture?

Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
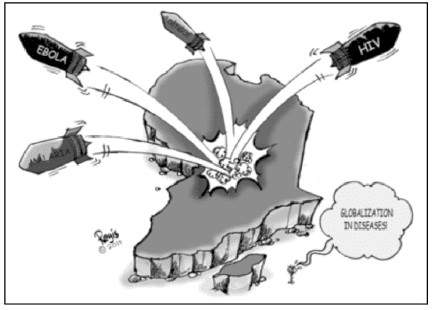
Q. How did globalization help in the medical field?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. What is given way recently by the old “Welfare state”?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. The increase in the MNCs all over the world has resulted in ....................... .
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of ......................... .
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. What do the new states withdraw as a result of globalisation?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. How globalisation should not be viewed?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. In terms of trade, what is the impact of globalisation?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. Where does economic globalisation draw our attention to?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. According to broader way of looking at globalisation, what should we focus on?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. In between which years the world’s export has increased 33-fold?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. After the 1980s, which policy was introduced by US and UK?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. We can see “a sharp increase” due to globalisation in ................................ ?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. What is the impact of an increase in the economic exchanges between the countries of the world?
|
34 videos|246 docs|52 tests
|


















