Test: Poverty as a Challenge (Term II) - Class 9 MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test Online MCQ Tests for Class 9 - Test: Poverty as a Challenge (Term II)
Assertion (A) : Social scientists look at poverty through a variety of indicators.
Reason (R) : Poverty has many facets.
Assertion (A) : People in urban areas do more physical work.
Reason (R) : Calorie requirement per person is more in rural areas than urban areas.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
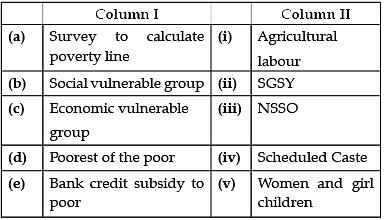
Match the correct answers of column I with column II.

Prime Minister Rozgar Yojna is an ________ programmes.
The accepted average calorie requirement in India is __________ calories per person per day in rural areas.
Assertion (A) : Poverty means hunger and lack of shelter.
Reason (R) : Poverty is living with a sense of hopelessness.
Assertion (A) : Caste system is prevalent in Indian society.
Reason (R) : Social exclusion reduces poverty.
_________ and ___________ are the poorest states in India.
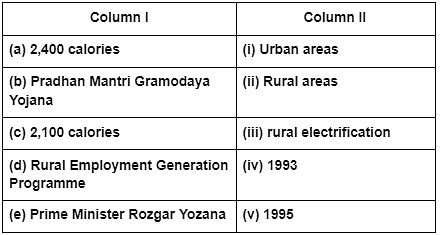
Match the correct answers of column I with column II.
A person is considered poor if his or her income or consumption level falls below a given __________ necessary to fulfill basic needs.
The poverty line is estimated periodically by conducting sample surveys carried out by the ______.
|
5 docs|314 tests
|












