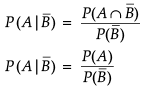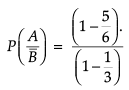Test: Probability- Assertion & Reason Type Questions - JEE MCQ
6 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 12 - Test: Probability- Assertion & Reason Type Questions
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A) : If A = A1 ∪ A2… ∪ An, where A1… An are mutually exclusive events then
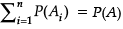
Reason (R) : Given, A = A1 ∪ A2 ... ∪ An
Since A1...An are mutually exclusive P(A) = P(A1) + P(A2)+ ….+P(An)
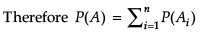
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A) : If A ⊂ B and B ⊂ A then, P(A) = P(B).
Reason (R) : If A ⊂ B then 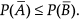
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A) : If A and B are two mutually exclusive events with 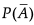 = 5/6 and P(B) = 1/3. Then
= 5/6 and P(B) = 1/3. Then 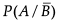 is equal to 1/4.
is equal to 1/4.
Reason (R) : If A and B are two events such that P(A) = 0.2, P(B) = 0.6 and P(A|B) = 0.2 then the value of 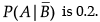
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A) : The probability of an impossible event is 1.
Reason (R) : If A is a perfect subset of B and P(A) < P(B), then P(B – A) is equal to P(B) – P(A).
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A) : Let A and B be two events such that the occurrence of A implies occurrence of B, but not vice-versa, then the correct relation between P(A) and P(B) is P(B) ≥ P(A).
Reason (R) : Here, according to the given statement![]() P(B) = P(A ∪ (A ∩ B)
P(B) = P(A ∪ (A ∩ B)
(∵ A ∩ B = A)
= P(A) + P(A ∩ B)
Therefore, P(B) ≥ P(A)
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as
Assertion (A): Let A and B be two events such that P(A) = 1/5 , while P(A or B) = 1/2. Let P(B) = P, then for P = 3/8 , A and B independent.
Reason (R) : For independent events, P(A ∩ B) = P(A) P(B)
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= P(A) + P(B) – P(A) P(B)
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ P = 3/8.
|
204 videos|290 docs|139 tests
|