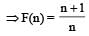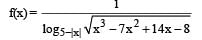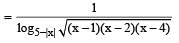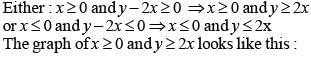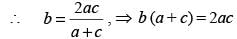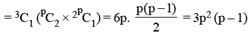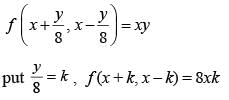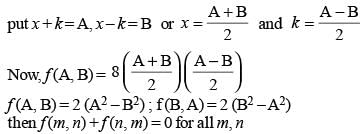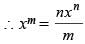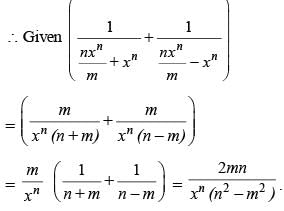Test: Functions - CAT MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise Past Year Questions for CAT - Test: Functions
Let f be a function such that f(mn) = f(m) f(n) for every positive integers m and n. If f(1), f(2) and f(3) are positive integers, f(1) < f(2), and f(24) = 54, then f(18) equals
(2019)
Let f(x) = min{2x2, 52 − 5x}, where x is any positive real number. Then the maximum possible value of f(x) is
(2018)
If f(x + 2) = f(x) + f(x + 1) for all positive integers x, and f(11) = 91, f(15) = 617, then f(10) equals
(2018)
The area of the closed region bounded by the equation |x| + |y| = 2 in the two-dimensional plane is
(2017)
Consider two figures A and D that are defined in the co-ordinate plane. Each figure represents the graph of a certain function, as
defined below:
A: | x | - | y | = a
D :| y | = d
If the are enclosed by A and D is O. Which of the following is a possible value of (a, d):
(2016)
If [log10 1] + [log10 2] + [log10 4] +...+ [log10 n] = n where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then
(2016)
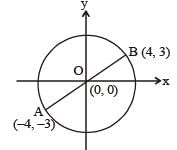
The coordinates of two diagonally opposite vertices of a rectangle are (4, 3) and (-4,-3). Find the number of such rectangle(s), if the other two vertices also have integral coordinates.
(2015)
‘f’ is a real function such that f(x + y) = f(xy) for all real values of x and y. If f(–7) = 7, then the value of f(–49) + f(49) is
(2014)
Let f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, where a, b and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. If f(x) attains its maximum value at x = 2, then what is the sum of the roots of f(x) = 0?
(2013)
If f(x) = (secx + cosecx)(tanx - cotx) and π/4 < x < π/2, then f(x) lies in the range of
(2013)
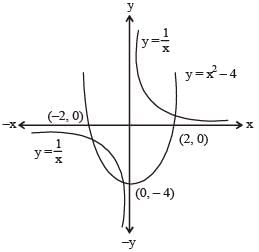
At how many points do the graphs of y = 1/x and y = x2 – 4 intersect each other?
(2013)
A function F(n) is defined as F(n - 1) = 1/(2 - F(n)) for all natural numbers ‘n’. If F(1) = 2, then what is the value of [F(1)] + [F(2)] +…………+ [F(50)]?
(Here, [x] is equal to the greatest integer less than or equal to ‘x’)
(2012)
A function f(x) is defined for real values of x as:
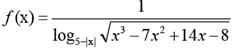
What is the domain of f(x)?
(2012)
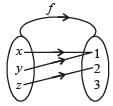
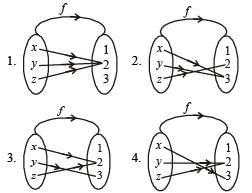
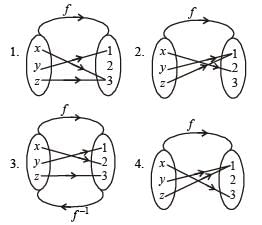
Let f be an injective map with domain{x, y, z} and range {1, 2, 3} such that exactly one of the following statements is correct and the remaining are false. f(x) = 1, f(y) ≠ 1, f(z) ≠ 2. The value of f –1(1) is
(2011)
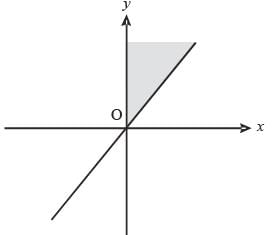
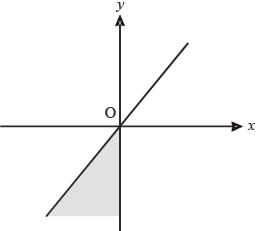
The shaded portion of figure shows the graph of which of the following?
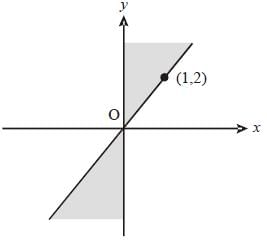
(2011)
When ‘2’ is added to each of the three roots of x3 – Ax2 + Bx – C = 0, we get the roots of x3 + Px2 + Qx – 18 = 0. A, B, C, P and Qare all non-zero real numbers. What is the value of (4A + 2B + C)?
(2011)
If three positive real numbers a, b and c (c > a) are in Harmonic Progression, then log (a + c) + log (a – 2b + c) is equal to:
(2010)
There are three coplanar parallel lines. If any p points are taken on each of the lines, then find the maximum number of triangles with the vertices of these points.
(2010)
If f (x + y/8, x - y/8) = xy, then f (m, n) + f (n, m) = 0
(2010)
If mxm – nxn = 0, then what is the value of 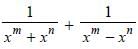 in terms of xn ?
in terms of xn ?
(2010)
|
43 docs|31 tests
|



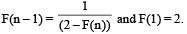
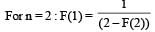
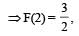
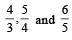 respectively..
respectively..