Test: Heat - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Heat
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
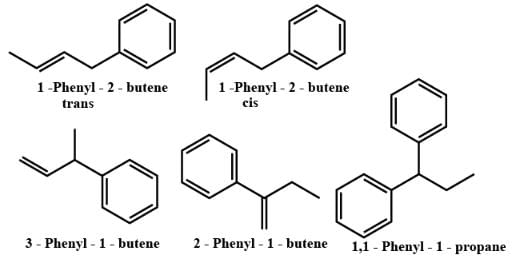
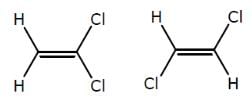
How many minimum no. of C-atoms are required for position & geometrical isomerism in alkene?
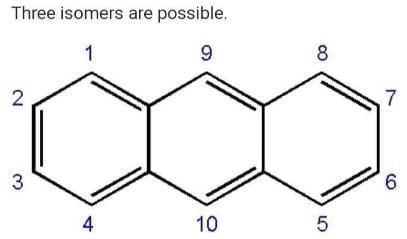
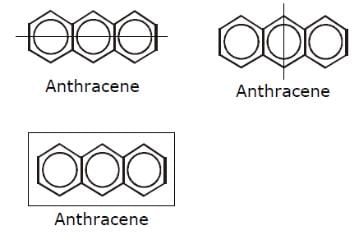
How many structural formula are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom in anthracene?
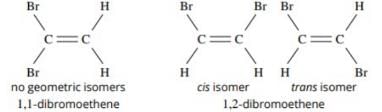
The number of isomers of dibromoderivative of an alkene (molear mass 186 g mol–1) is
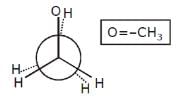
Increasing order of stability among the three main conformation (i.e. eclipse, anti, gauche) of ethylene glycol is:
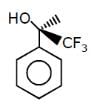
Which of the follownig compounds is (S)–4-chloro-1-methylcyclohexene ?
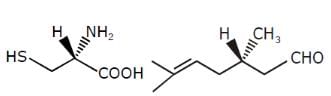
Which of the following compounds has two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbons) ?
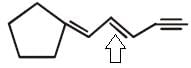
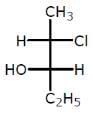
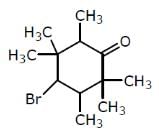
Examine the compound on the right. How many stereoisomers having this constitution are possible ?
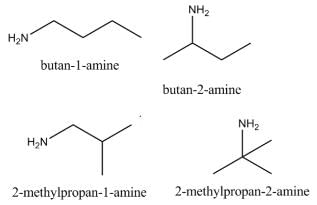
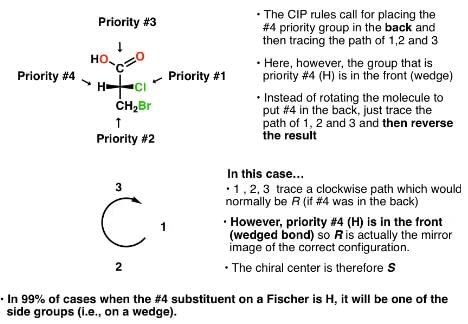
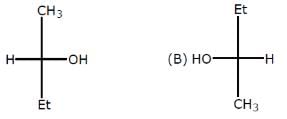
Which of the following heptanols are chiral 1-heptanol, 2-heptanol, 3-heptanol, 4-heptanol.
Minimum C atoms required for a compound to show geometrical isomerism :
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|