Test: Potential Energy - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Potential Energy
How much work is done by a man weighing 80 kgf in raising a stone of weight 20 kgf to the top of a building of height 40 m? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
The potential energy of a body at height h is mgh. Then its kinetic energy just before hitting the ground is
In the given figure, what is the work done by the spring force?
A body dropped from height H reaches the ground with a speed of 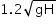
You are in a lift moving from the 3rd floor to the 12th floor, through a height H. If the elevator moves at a constant speed without stopping, what is the work performed on you by the elevator? Take your body mass as M.
An astronomer has total weight of 80 kg. On reaching moon, he climbs up 10 m to enter his aircraft by the ladder. His gravitational potential energy is increased by 1000 J. The value of the gravitational acceleration on the moon is
Out of a pair of identical springs of spring constants 240 N/m, one is compressed by 10 cm and other is stretched by 10 cm. The difference in P.E. stored in the two springs is:
What is the dimension of k/m where k is the force constant and m is the mass of the oscillating object?
A ball of mass 2 kg is raised to the height of 60 m and then dropped from the top. In this case, the quantity which has different magnitude from the other given quantities is
A hawk of mass 10 kg dives to catch a mouse. During dive it loses 500 J of its potential energy. The height from where it begins its dive is (take g = 10 m/s2)
A vehicle of 50 quintal climbs up a hill of 10 m. The potential energy gained by it is (take g = 10 m/s2)
You are in a lift moving from the 3rd floor to the 12th floor, having a height difference of H = 40 m. Your mass is M = 80 kg and the acceleration due to gravity is g = 10 m/s2. If the elevator moves at a constant speed without stopping, what is the total work performed by all of the forces together (the net force) acting on you?
An elastic spring of force constant k is compressed by an amount x. Then its potential energy will be
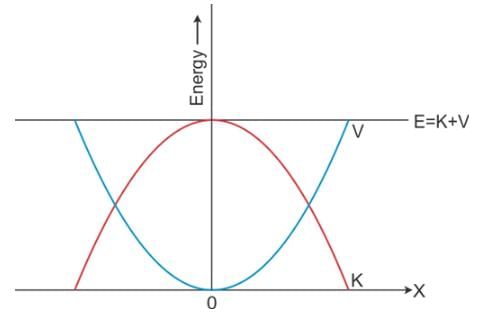
A plot of potential energy and kinetic energy versus displacement x for a block attached to a spring obeying Hooke’s law is