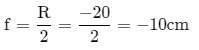Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 2
A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
A point object is kept in front of a plane mirror. The plane mirror is doing SHM of amplitude 2cm. The plane mirror moves along the x-axis and x-axis is normal to the mirror. The amplitude of the mirror is such that the object is always infront of the mirror. The amplitude of SHM of the image is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A watch shows the time as 3 : 25. What will be the time that appears when seen through a plane mirror ?
If a ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle 60° from the mirror surface, then deviation produced by mirror is
When light is reflected from a mirror a change occurs in its
The images of clouds and trees in water always less bright than in reality
A rays is incident at an angle 38º on a mirror. The angle between normal and reflected ray is
A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
Which of the following letters do not surface lateral inversion
An object is initially at a distance of 100 cm from a plane mirror. If the mirror approaches the object at a speed of 5 cm/s. Then after 6 s the distance between the object and its image will be
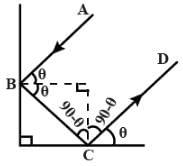
Two mirrors are placed perpendicular to each other. A ray strikes the first mirror and after reflection from the first mirror it falls on the second mirror. The ray after reflection from second mirror will emerge
A person is in a room whose ceiling and two adjacent walls are mirrors. How many images are formed?
If an object is placed unsymmetrically between two plane mirrors, inclined at the angle of 600, then the total number of images formed is
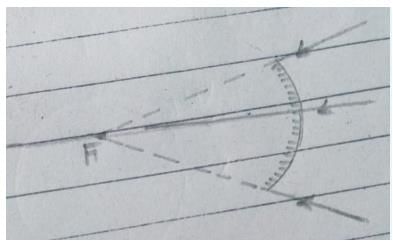
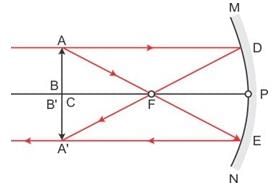
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
A concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm forms image of the sun. The diameter of the sun subtends an angle 1° on the earth. Then the diameter of the image is (in cm)
A convex mirror has a focal length f. A real object, placed at a distance f in front of it from the pole, produces an image at
A convex mirror has a focal length = 20 cm. A convergent beam tending to converge to a point 20 cm behind convex mirror on principal axis falls on it. The image if formed at
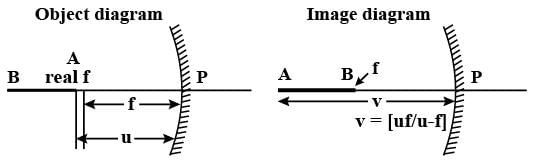
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is received on a screen placed at a distance of v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between 1/v versus 1/u is
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. The near end of the rod is at a distance u > f from the mirror. Its image will have a length
The radius of curvature for a convex lens is 40 cm, for each surface. Its refractive index is 1.5. The focal length will be
A concave mirror gives an image three times as large as the object placed at a distance of 20 cm from it. For the image to be real, the focal length should be
If an object is 30 cm away from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, the image will be
The largest distance of the image of a real object from a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm can be
A particle is moving towards a fixed spherical mirror. The image :
A straight line joining the object point and image point is always perpendicular to the mirror
The focal length of spherical mirror is
A virtual image, larger than the object can be produced by
In case of concave mirror, the minimum distance between a real object and its real image is :
|
97 videos|336 docs|104 tests
|