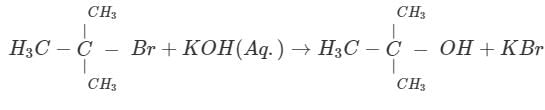Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 1
Which of the following statements regarding the E2 mechanism is wrong?
The major product P formed in the given reaction is:
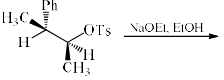
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Predict the major product P in the following reaction:
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
The major product obtained on treatment of the following compound with H2SO4 at 80°C is:
In the following compound, the hydroxy group that is most readily Methylated with C2H2N2 is:
The major product formed in the following reaction is :
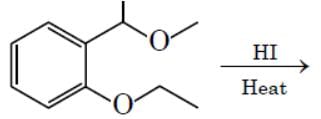
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
In the cyclisation reaction given below, the most probable product formed is:
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
The body of car is repaired with help of a filler which is hardened by addition of:
The correct order of reactivity of p-halonitrobenzens in the following reaction is:
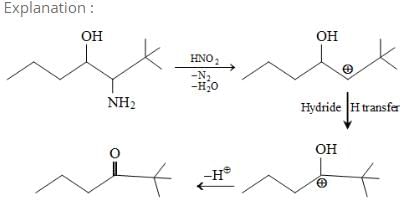
Solvolysis of the optically active compound X gives, mainly:
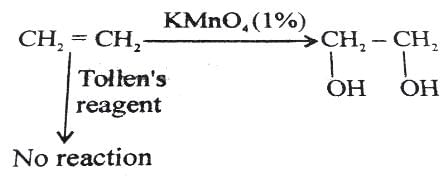
The major product obtained in the following reaction, is:
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Increasing order of stability of following carbocations (give least stable first)?
(I) Tropylium
(III) (C6H5)2C+
(IV) CH3+
What is the nucleophilicity order for SN2 reaction:
(I) C6H5S–
(II) C2H5O–
(III) NO3–
(IV) CN–
(V) I–
Select order of effectiveness of Lewis acid catalyst in Friedel-Crafts reaction:
For the reaction between alkyl halide and OH- increase in solvent polarity generally:
Reactive intermediate formed in the following reaction is:
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon atom of a dextro alkyl halide always gives a:
Reaction of ethyne with HCN in presence of Ba (CN)2 is an example of:
Consider the following carbocations, most stable is:
The major product formed in the reaction given below is: