Test: Rocks And Minerals - 2 - Class 5 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 5 - Test: Rocks And Minerals - 2
Read the given statements
Statement I: Clay is the smallest particle of soil.
Statement II: Sand is the smallest particle of soil.
Q. Which of the following is correct about the above statements?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The rock used for building materials like tiles and bricks is made from
Regarding soil, which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following rocks are known as fiery rock?
Which of the following natural resources provides raw materials for plastic paint, fertilizers and cosmetics?
Black gold is the name given to which natural resource?
Fossil fuels are formed over a long period of time, because of heat and pressure. What was the original things which gets converted to fossil fuels?
Composition of air is given in the following graph
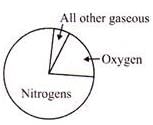
Q. Which of the following is correct?
A large part of forest was cleared by burning. What it will happen to the area?
Which of the following factors is not responsible for exhaustion of natural resources?
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|

















