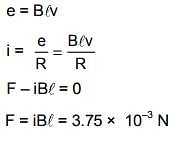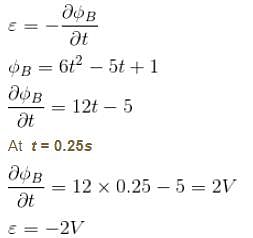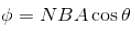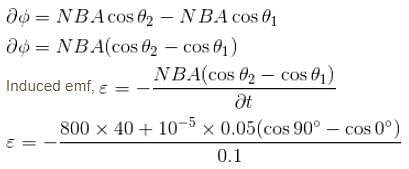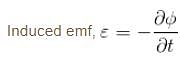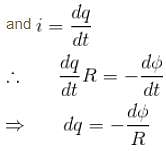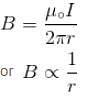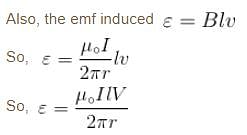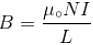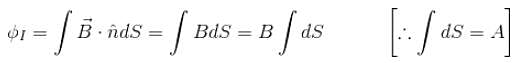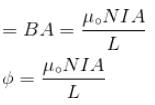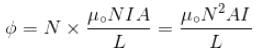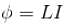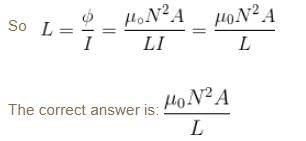Faraday's Law MCQ Level - 1 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Faraday's Law MCQ Level - 1
The induced emf in a coil rotating in a uniform magnetic field depend upon.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends.
A metallic rod completes its circuit as shown in the figure. The circuit is normal to a magnetic field of B = 0.15 tesla. If the resistances of the rod is 3Ω the force required to move the rod with a constant velocity of 2 m/sec is -
A coil of metal wire is kept stationary in a uniform magnetic field :
The magnetic flux φ (in weber) in a closed circuit of resistance 10Ω varies with time t (in second) according to equation φB = 6t2 - 5t + 1. The magnitude of induced current at t = 0.25sec is :
A coil has an area of 0.05 m2 and it has 800 turns. It is placed perpendicularly in a magnetic field of strength 4 × 10–5 wb/m2. It is rotated through 90° in 0.1s. The average emf induced in the coil is :
A magnet is brought towards a coil (i) speedily and (ii) slowly then the induced emf/induced charge will be respectively.
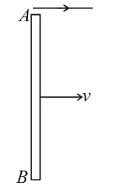
The current carrying wire and rod AB are in the same plane. The rod moves parallel to the wire with a velocity v. Which one of the following statement is true about induced emf in the rod.
The self inductance of solenoid of length L area of cross-section A and having N turns is