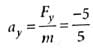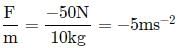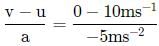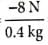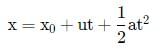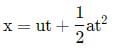Test: Newton's Second Law of Motion (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - Test: Newton's Second Law of Motion (NCERT)
Which one of the following statemenls is not true about Newtons second law of motion 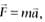
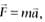
The relation 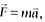 , cannot be deduced from Newton's second law, if
, cannot be deduced from Newton's second law, if
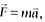 , cannot be deduced from Newton's second law, if
, cannot be deduced from Newton's second law, ifA large force is acting on a body for a short time. The impulse imparted is equal to the change in:
Which one of the following is not force?
The motion of particle of mass m is given by y = ut + 1/2gt2. The force acting on the particle is
A constant force acting on a body of mass of 5 kg change its speed from 5ms-1 to 10ms-1 in 10s without changing the direction of motion, 'The force acting on the body is
A bullet of mass 40g moving with a speed of 90 ms-1 enters a heavy wooden block and is stopped after a distance of 60 cm. The average resistive force exerted by the block on the bullet is
A body under the action of a force 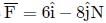 acquiring an acceleration of 5ms−2. The mass of the body is
acquiring an acceleration of 5ms−2. The mass of the body is
A body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity 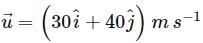 . If a constant force
. If a constant force 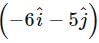 N acts on the body, the time in which the y -component of the velocity becomes zero is
N acts on the body, the time in which the y -component of the velocity becomes zero is
A constant retarding force of -50 N is applied to a body of mass 10 kg moving initially with a speed of 10 m s-1.The body comes to rest after
A body of mass 0.4 kg starting at origin at t = 0 with a speed of 10 m s-1 in the positive x-axis direction is subjected to a constant F = 8 N towards negative x-axis. The position of the body after 25 s is
If the force on a rocket, moving with a velocity of 300 m s-1 is 210 N, then the rate of combustion of the fuel is
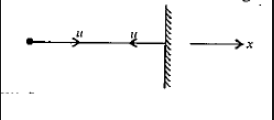
A ball of mass m strikes a rigid wall with speed u and rebounds with the same speed. The impulse imparted to the ball by the wall is
A batsman hits back a ball of mass 0,15 kg straight in the direction of the bowler without changing its initial speed of 12 m s-1. If the ball moves linearly, then the impulse imparted to the ball is
|
257 docs|234 tests
|



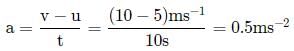
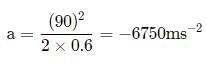
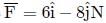 and a = 5ms−2
and a = 5ms−2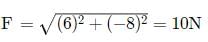
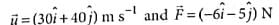 ∴ uy = 40 m s-1 and Fy = -5 N
∴ uy = 40 m s-1 and Fy = -5 N