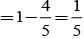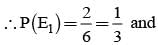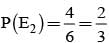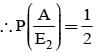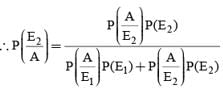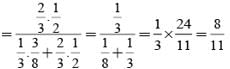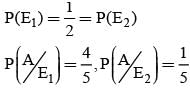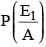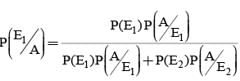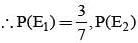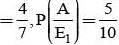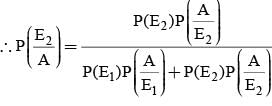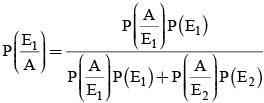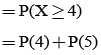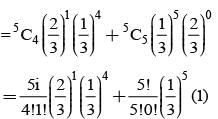JEE Advanced Level Test: Probability- 1 - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve - JEE Advanced Level Test: Probability- 1
A coin is tossed n times. The probability of getting head at least once is greater than 0.8. Then the least value of n is
A and B throw a coin alternately till one of them gets a ‘head’ & wins the game. If A has the first threw, then the probabilities of winning for A and B are respectively.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If the probabilities that A&B will die within a year are x & y respectively, then the probability that exactly one of them will be alive at the end of the year is
Two integers are selected at random from integers 1 to 11. If the sum is even, find the probability that both the numbers are odd.
A letter is known to have come either from TATANAGAR or from CALCUTTA. On the envelope just two consecutive letters TA are visible. What is the probability that the letters came from TATANAGAR ?
There are 5% defective items in a large bulk of items. What is the probability that a sample of 10 items will include not more than one defective item?
Six boys and six girls sit in a row at random. Then the probability that six girls sit together is
The probability for a randomly chosen month to have its 10th day as Sunday is
A person writes 4 letters and addresses 4 envelopes. If the letters are placed in the envelopes at random, then the probability that all letters are not placed in the right envelope is
A bag contains 5 brown and 4 white socks. A man pulls out 2 socks. The probability that they are of the same colour is:
From a group of 5 boys and 3 girls, 3 persons are chosen at random. Then the probability that there are more girls than boys is:
Out of 15 tickets marked 1, 2, 3, ... 15, three are drawn at random. The chance that numbers on them are in AP is
Vishnu, Tarun and Amit in order toss a coin. One who throws head first, wins the game. Their respective chances of winning are:
Three of the six vertices of a regular hexagon are chosen at random. The probability that the triangle with these vertices is equilateral is:
A bag contains 50 tickets numbered 1, 2, 3 ... 50, of which five are drawn at random and arranged in ascending order of magnitude (x1< x,< x3< x4< x5), the probability that x3 = 30 is
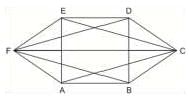
In a competition; A, B, C are participating. The probability that A wins is twice that of B and the probability that B wins is twice that of C. The probability that A loses is
A speaks truth in 75% cases and B speaks truth in 80% cases. The probability that they contradict each other in a statement is
A purse contains 4 copper and 3 silver coins; and a second purse contains 6 copper and 2 silver coins. If a coin is taken from one of the two purses, then the probability that it is a copper coin is
A die is thrown three times. If the first throw is a four, find the choice of getting 15 as the sum
Suppose a girl throws a die. If she gets a 5 or 6, she tosses a coin three times and notes the number of heads. If she gets 1, 2, 3 or 4. She losses a coin once and notes whether a head or tail is obtained. If she obtained exactly one head, what is the probability that she threw 1, 2, 3 or 4 with the die?
Probability that A speaks truth is 4/5. A coin is tossed, a reports that a head appears. The probability that actually there was head is
Bag I contains 3 red and 4 black balls and bag II contains 4 red and 5 blacks’ balls. One ball is transferred from Bag I to Bag II and then a ball is drawn from Bag II. The ball so drawn is found to be red. Find the probability that the transferred ball is black
A card from a pack of 52 cards is lost. From the remaining cards of the pack, two cards are drawn and are found to be both diamonds. Find the probability that the lost card was a diamond:
In answering a question on a multiple choice test, a student either knows the answer or guesses. Let 3/4 be the probability that he knows the answer and 1/4 be the probability that he guesses. Assuming that a student who guesses at the answer will be correct with probability 1/4. What is the probability that the student knows the answer given that he answered it correctly?
On a multiple choice examination with three possible answers for each of the five questions, what is the probability that a candidate would get four or more correct answers just by guessing?
Words from the letters of the word PROBABILITY are formed by taking all letters at a time. The probability that both B’s are not together and both I’s are not together is
In a n-sided regular polygon, the probability that the two diagonal chosen at random will intersect inside the polygon is
A coin is tossed 7 times. Then the probability that at least 4 consecutive heads appear is
The probability that a random chosen three-digit number has exactly 3 factor is
Five different games are to be distributed among 4 children randomly. The probability that each child get atleast one game is
|
141 videos|213 docs|254 tests
|
|
141 videos|213 docs|254 tests
|


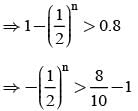
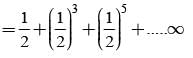
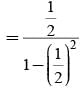
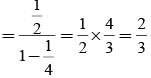
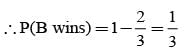
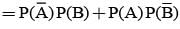
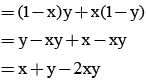
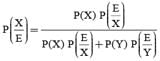
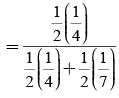
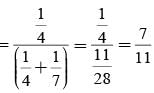
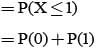
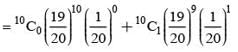
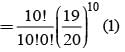
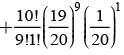
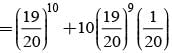
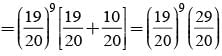
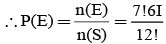
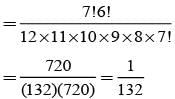
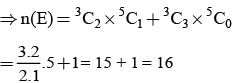
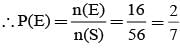
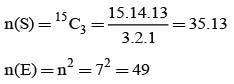
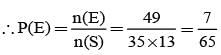
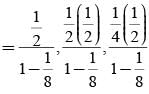
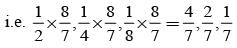
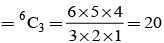
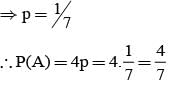
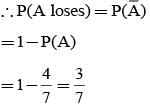
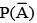 = P(A tells a lie)
= P(A tells a lie) 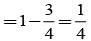
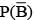 = P(B tells a lie)
= P(B tells a lie)