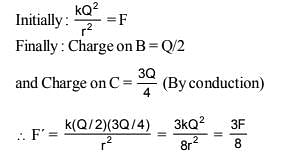Test: Electrostatics of Conductors - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Electrostatics of Conductors
Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and carrying equal charges repel each other witha force F when kept apart at some distance. A third spherical conductor having same radius as that of B but uncharged is brought in contact with B, then brought in contact with C and finally removed awayfrom both. The new force of repulsion between B and C
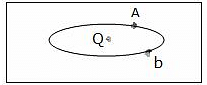
As shown in the figure below, an ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge Q is placed at the centre of the cavity. If points A and b are shown on the cavity surface (see figure), then which among the following choices is correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to
Electrostatic field is zero_____ the conductor.
Some charge is being given to a conductor. Then its potential:
The value of electric potential throughout the volume of a conductor is
How does the charge densities of conductors vary on an irregularly shaped conductor?
Two conductors having same type of charges are connected by a conducting wire. There would not be any amount of charges on them if:
Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then,
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|