Test: Physical Properties & General Reactions - NEET MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Physical Properties & General Reactions
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?
What would be the major product in the following reaction?
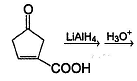
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following on reaction with excess of NaHSO3 in aqueous solution will give mixture of salts which can be separated into two fractions by fractional crystallisation?
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?
The reagent which can best bring about the following transformation is
The most probable product of the following reaction is
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The most likely organic product X is
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The most likely organic product X is
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-13) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The organic product(s) formed above is/are
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
The correct observation regarding the above reaction is/are
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
The correct deduction(s) regarding the above reagent is/are
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct deduction(s) regarding mechanism of the above reaction is/are
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 14-16) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
The structure of A satisfying the above criteria is
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
The correct statement regarding the compound D is
One integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-22) This section contains 6 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
If all the aldehyde isomers of C5H10O is independently treated with HCN/NaCN solution, how many of them will give racemic mixture of cyanohydrin?
If one molecule of trioxane is heated, how many molecules of formaldehyde would be formed?
A mixture containing all isomeric cyclohexanedione is treated with excess of NaHSO3 solution. How many different disulphite salts are formed?
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
How many deuterium would be incorporated in the final product?
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
X is formed in which a new ring is formed. How many atoms are present in this new ring?
Matching List Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 23 and 24) Choices for the correct combination o f elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the reactants from Column I with the reagents and expected outcomes from Column II. Mark the correct option form the codes given below.
Match the reactions from Column I with the properties of products from Column II. Mark the correct option form the codes given below.
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|


















