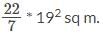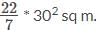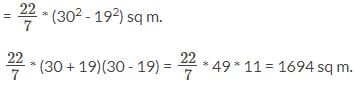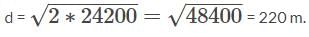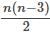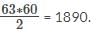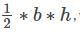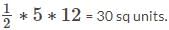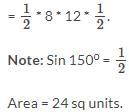Test: Area Of Circles - GRE MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Reasoning for GRE - Test: Area Of Circles
The length of a rope, to which a cow is tied, is increased from 19m to 30m. How much additional ground will it be able to graze? Assume that the cow is able to move on all sides with equal ease. Use π = 22/7 in your calculations.
A lady grows cabbages in her garden that is in the shape of a square. Each cabbage takes 1 square feet of area in her garden. This year, she has increased her output by 211 cabbages as compared to last year. The shape of the area used for growing the cabbages has remained a square in both these years. How many cabbages did she produce this year?
The area of a square field is 24200 sq m. How long will a lady take to cross the field diagonally at the rate of 6.6 km/hr?
A wheel of a car of radius 21 cms is rotating at 600 RPM. What is the speed of the car in km/hr?
A cube of side 5 cm is painted on all its side. If it is sliced into 1 cubic centimer cubes, how many 1 cubic centimeter cubes will have exactly one of their sides painted?
Is triangle ABC with sides a, b and c acute angled?
Triangle with sides a2, b2, c2 has an area of 140 sq cms.
Median AD to side BC is equal to altitude AE to side BC.
Is triangle ABC obtuse angled?
a2 + b2 > c2
The center of the circle circumscribing the triangle does not lie inside the triangle.
If 10, 12 and 'x' are sides of an acute angled triangle, how many integer values of 'x' are possible?
What is the radius of the incircle (circle inscribed) of the triangle whose sides measure 5, 12 and 13 units?
If the sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon measures 1440o, how many sides does the polygon have
What is the measure of the radius of the circle that circumscribes a triangle whose sides measure 9, 40 and 41?
What is the area of an obtuse angled triangle whose two sides are 8 and 12 and the angle included between two sides is 150o?
Vertices of a quadrilateral ABCD are A(0, 0), B(4, 5), C(9, 9) and D(5, 4). What is the shape of the quadrilateral?
|
93 videos|77 docs|104 tests
|