Test: Cache Memory- 2 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Computer Science Engineering(CSE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Cache Memory- 2
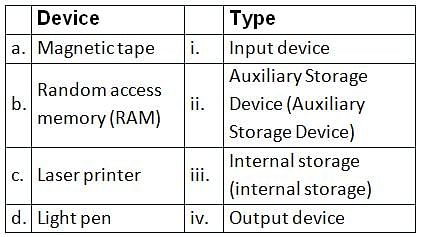
Which of the following is NOT a part of auxiliary memories in a Computer system?
Which one of the following memory units is considered as the largest?
Which of the following memory devices is very much similar, mainly in terms of speed, to the cache memory?
Which among the following memories is used in Digital camera?
Which of the following is a Permanent Memory in the computer?
Which memory cannot be accessed directly by the CPU of the computer?
The actual timing signals that govern the transfer of data between input unit, processor, memory and output units are generated by the ________ and the ______ stores the processed data.
The primary memory (also called main memory) of a personal computer consists of
The Boot sector files of the system are stored in which computer memory?
Which of the following has the fastest speed in the computer memory hierarchy?
Which process is used to map logical addresses of variable length onto physical memory?
Which computer memory chip allows simultaneous both read and write operations?
In which type of memory, once the program or data is written, it cannot be changed?
Which of the following statements are not correct about the main memory of a computer?
|
55 docs|215 tests
|
|
55 docs|215 tests
|