Test: Geometry- 3 - CAT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - Test: Geometry- 3
The line AB is 6 m, in length and is tangent to the inner of the two concentric circles at point C. It is known that the radii of the two circles are integers. The radiusof the outer circle is-------, where A and B are points on the outer circle.
Two chords of lengths a and b of a circle subtend 60° and 90° angles at the centre respectively. Which of the following is correct?
A chord of length 32 cm is placed inside a circle of radius 20 cm and a point whose distance from the centre of the circle is 13 cm, is marked on the chord. Calculate the lengths of the segment of the chord.
The biggest possible regular hexagon H is cut out of an equilateral triangle X. The biggest possible equilateral triangle Y is cut out from the hexagon H. What is the ratio of the areas of the equilateral triangles X and Y?
In any quadrilateral ABCD, the diagonal AC and BD intersect at a point X. If E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AX, BX, CX and DX respectively, then what is the ratio of (EF + FG + GH + GE) to (AD + DC + CB + BA)?
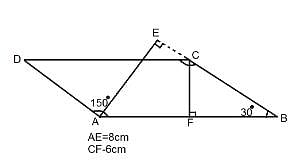
One of the angles of a parallelogram is of 150°. Altitudes are drawn from the vertex of this angle. If these altitudes measure 6 cm and 8 cm, then find the perimeter of the parallelogram.
Let C1 and C2 be the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle with sides 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm.
PQRS is a trapezium with PQ and RS parallel. PQ = 6 cm, QR = 5 cm, RS = 3 cm, PS = 4 cm. The area of PQRS is
A ball of diameter 15 cm is floating so that the top of the ball is 5 cm above the smooth surface (water) of the pond. What is the circumference in centimeters of the circle formed by the contact of the water surface with the ball?
Two circles APQC and PBDQ intersect each other at the points P and Q and APB and CQD are two parallel straight lines. Then only one of the following statements is always true. Which one is it?
Three horses are grazing within a semi-circular field. In the diagram given below, AB is the diameter of the semi-circular field with centre at O. Horses are tied up at P, R and S such that PO and RO are the radii of semi-circles with centres at P and R respectively and S is the centre of the circle touching the two semi-circles with diameters AO and OB. The horses tied at P and R can graze within the respective semi-circle and the horse tied at S can graze within the circle centered at S. The percentage of the area of the semi-circles with diameter AB that cannot be grazed by the horses is nearest to
Consider the following figure: AB = 10 cm, AC = 17 cm, BC = 21 cm and EHFD is a square. Find the length of the side of square (in cm).
For a regular octagon inscribed in a circle of radius 1 cm, the product of the distance from a fixed vertex to the other seven vertices is
A ring of diameter 10 cm is suspended from a point 12 cm vertically above the centre by six equal strings. The strings are attached to the circumference of the ring at equal intervals, thus keeping the ring in a horizontal plane. The value of cosine of the angle between the two adjacent strings lies in between
|
191 videos|133 docs|110 tests
|