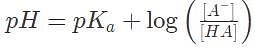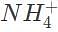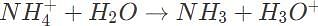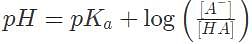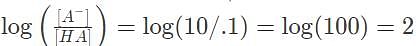Test: Acid/base Equilibria - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test General Chemistry for MCAT - Test: Acid/base Equilibria
Hypochlorous acid dissociates in water to create hydronium ions and hypochlorite ions HOCl + H2O ⇔ H3O+ + OCl- Suppose that additional hypochlorite ions are added to the solution. Which of the following correctly describes the resultant effect on the concentration of HOCl?
Suppose an equilibrated, dilute solution containing an acid H A with Kα = 10-4 is measured to have pH = 6 and [HA] = 10-8 M. Which of the following gives the best estimate of [A-]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Suppose a weak acid has Kα = 4.0 x 10-9. Which of the following gives its equivalent Kb ?
Which of the following best describes a chemical species that is measured to have Kb = 3.2 x 10-18?
Suppose a large organic molecule X is classified as a Lewis acid, while another large molecule Y is classified as a Bronsted-Lowry acid. Which of the following most accurately describes a similarity in their behaviors in solution?
Which of the following describes the pH of an equilibrated, stoichiometric mixture of ammonia, NH3 and hydrochloric acid HCl
Suppose a nanotechnological innovation allows every single charged ion to be precisely identified and removed from a small volume of water. Which of the following describes Kα for the water at the end of the process, assuming that the filtered water is given adequate time to re-equilibrate?
Suppose an acid H A has a dissociation constant Kα = 1 x 10-1. It is mixed into a buffered solution, and its equilibrium concentration is [H A] = .1M. If the concentration of its conjugate base is 10 M, what is the pH of the solution?
What is the pH of a solution with a hydronium ion concentration
[H3O+] = 104 M
Which of the following would have the weakest conjugate acid?
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|