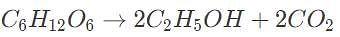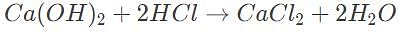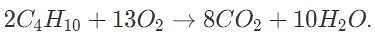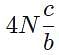Test: Stoichiometry - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test General Chemistry for MCAT - Test: Stoichiometry
One type of anaerobic respiration converts glucose (C6H12O6) to ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide. If the molecular weight of glucose is 180 grams/mol and the molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 1 mol of glucose is digested via respiration?
When an antacid tablet is used, calcium hydroxide interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form inert calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. If the molar mass of (Ca(OH)2 is 75 grams/mol, how many mols of HCl are required to fully react with 150 g of Ca(OH)2?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Measurements of a compound reveal that it is 36% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 48% oxygen, with systematic error accounting for the remaining 10%. Which of the following is the most accurate empirical formula for this compound?
In an unknown compound, the molar ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is found to be, respectively, 1:2:1. The molar mass is separately found to be 180 grams/mol. Which of the following gives the molecular formula of the compound?
Avogadro’s law states that one mole of an ideal gas takes up around 22 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Assuming all reagents can be treated as ideal gases, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced in the complete reaction of 44 liters of butane (C4H10), with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (at STP)?
Suppose 12 × 1023, atoms of sodium metal react stoichiometrically with chlorine gas. How many grams of sodium chloride will result if the molar mass of sodium chloride is 60 g/mol?
The general form of a synthesis reaction is αX + bY→ cZ, where capital letters denote reactants and lowercase letters denote balanced coefficients, a < b. Which of the following formulas gives the number of Z molecules produced when 4 mols of Y react completely? N is Avogadro’s number
Suppose 1 mol of H2 completely reacts with 1 mol of O2 to form water. How many mols of water will result from the reaction?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
Suppose that an industrial chemist wishes to obtain calcium chloride (CaCl2) by reacting calcium metal with chlorine gas. For safety reasons, she wishes to design the reaction to ensure that all of the chlorine gas is used in synthesis. Which of the following methods will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction?
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|