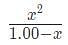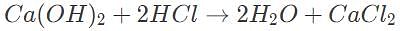Test: Titrations - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test General Chemistry for MCAT - Test: Titrations
33 mL of 3 M Hydrochloric acid is titrated with sodium hydroxide to form water and sodium chloride. How many mmols of sodium hydroxide are consumed in this reaction?
50 mL of 0.5 M barium hydroxide is required to fully titrate a 100 mL solution of sulfuric acid. What is the initial concentration of the acid?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a titration of a weak acid with a strong base, what is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point?
Which of the following describes the equivalence point on a graph of pH versus the amount of titrant added to a solution?
1 M of a weak acid H Z with Kα = 10e - 8 equilibrates in water according to the equation H Z + H2O → H3O+ + Z-. What is the pH of the solution at equilibrium?
Titration curves exhibit an asymptote at very large volumes of added titrant. Which of the following experimental parameters determines the location of this asymptote?
Which of the following criteria accurately describes the primary difference between a strong versus weak acid?
Which of the following describes the “buffer” region in a titration curve?
10 mL of 0.5 M calcium hydroxide is required to titrate 50 mL hydrochloric acid. Which of the following gives the initial concentration of the acid?
Which of the following pH indicator ranges would be the most useful for the titration of a weak base with a strong acid?
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|


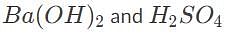
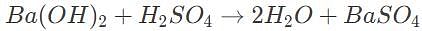
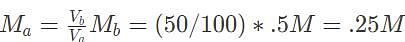
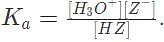 Substituting our values into this expression results in the equation 10e - 8 =
Substituting our values into this expression results in the equation 10e - 8 =