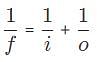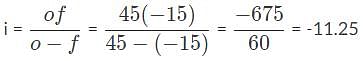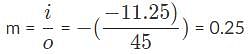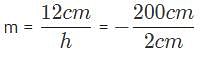Test: Thin Lenses - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics for MCAT - Test: Thin Lenses
During an experiment, a thin-lens system in its initial state produces a real, inverted, and enlarged image and in its final state produces a virtual, upright, and enlarged image. Which of the following statements best elucidates on what kind of change occurred for the thin-lens system?
Which of the following statements accurately describes an image formed by a thin converging lens?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
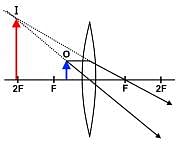
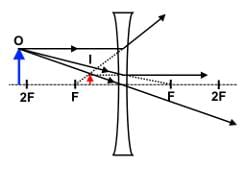
Which of the following statements best describes the image produced by a concave lens?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the sign conventions used for the thin lens equation?
When an object is placed 45 centimeters in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 15 centimeters, what are the image distance and the magnification?
What is the height of the image of an apple (h = 12 cm) sitting 2 meters away that is projected onto your retina if the focal length of the retina is 20 millimeters?
Two lenses that are 30 centimeters apart are used to form an image. Lens 1 has a focal length f1 = -5.0 cm, and lens 2 has a focal length f2 = 15 cm. The object is placed 20 centimeters to the left of Lens 1. Which of the following statements best describes the image formed?
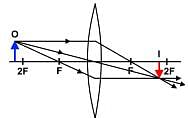
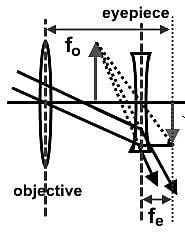
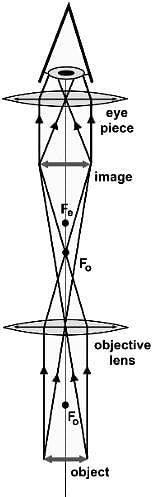
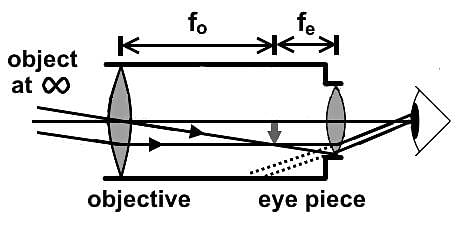
Which of the following statements best describes the schematic of the astronomical telescope below?
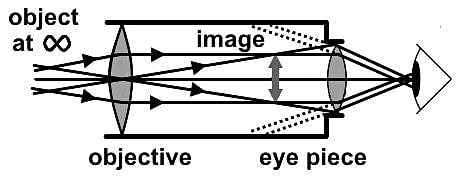
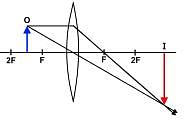
Which of the following statements does NOT accurately describe the schematic of the compound microscope below?
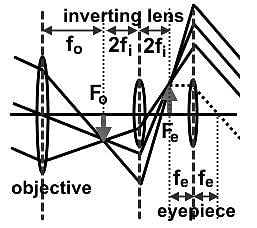
One of the challenges of using an astronomical telescope for terrestrial use is the production of an inverted image. Which of the following changes to the astronomical telescope would invert the image for terrestrial use?
|
158 videos|9 docs|21 tests
|