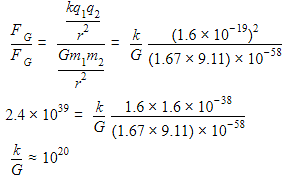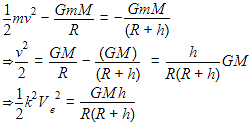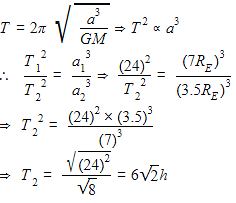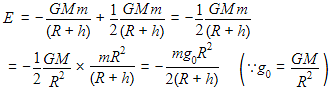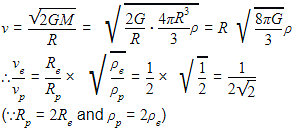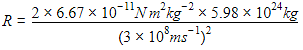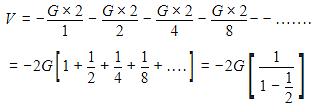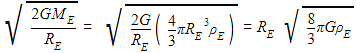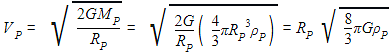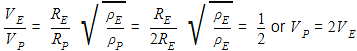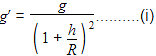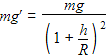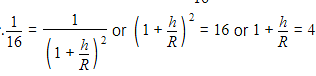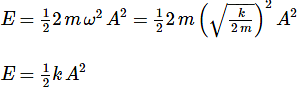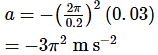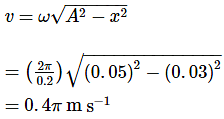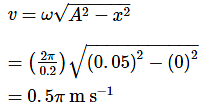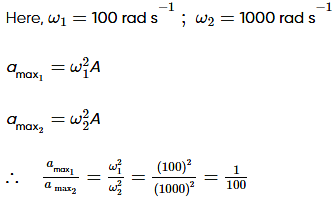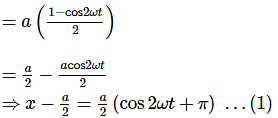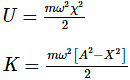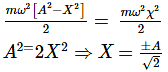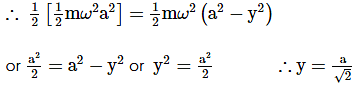NEET Minor Test - 4 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test NEET Mock Test Series 2025 - NEET Minor Test - 4
A body of mass 60g experiences a gravitational force of 3.0N, when placed at a particular point. The magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is
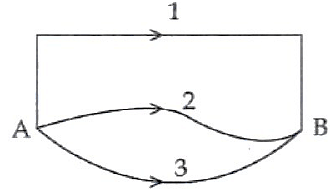
A gravitational field is present in a region and a mass is shifted from A to B through different paths as shown. If W1 W2 and W3 represent the work done by the gravitational force along the respective paths, then:

The ratio of Coulomb's electrostatic force to the gravitational force between an electron and a proton separated by some distance is 2.4 × 1039. The ratio of the proportionality constant, 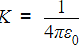 to the Gravitational constant G is nearly (Given that the charge of the proton and electron each =1.6 × 10−19C, the mass of the electron = 9.11 × 10−31kg, the mass of the proton = 1.67×10−27kg ) :
to the Gravitational constant G is nearly (Given that the charge of the proton and electron each =1.6 × 10−19C, the mass of the electron = 9.11 × 10−31kg, the mass of the proton = 1.67×10−27kg ) :
A particle of mass ' m ' is projected with a velocity v = kVe (k < 1) from the surface of the earth. (Ve = escape velocity) The maximum height above the surface reached by the particle is
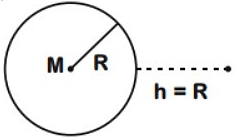
The work done to raise a mass m from the surface of the earth to a height h, which is equal to the radius of the earth, is
The time period of a geostationary satellite is 24h, at a height 6RE(RE. is radius of earth) from surface of earth. The time period of another satellite whose height is 2.5RE from surface will be,(
If the mass of the Sun were ten times smaller and the universal gravitational constant were ten times larger in magnitude, which of the following is not correct?
Two astronauts are floating in gravitational free space after having lost contact with their spaceship. The two will
A satellite of mass m is orbiting the earth (of radius R) at a height h from its surface. The total energy of the satellite in terms of g0, the value of acceleration due to gravity at the earth’s surface, is
The ratio of escape velocity at earth (ve) to the escape velocity at a planet (vp) whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is
A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The mass of the satellite is very small compared to the mass of the earth. Then,
A black hole is an object whose gravitational field is so strong that even light cannot escape from it. To what approximate radius would earth (mass = 5.98 × 1024kg) have to be compressed to be a black hole?
Infinite number of bodies, each of mass 2 kg are situated on x-axis at distances 1 m, 2 m, 4 m, 8 m ,..., respectively, from the origin. The resulting gravitational potential due to this system at the origin will be
The radius of a planet is twice the radius of earth. Both have almost equal average mass-densities. VP and VE are escape velocities of the planet and the earth, respectively, then
The height at which the weight of a body becomes 1/16th its weight on the surface of earth (radius R), is
The total mechanical energy of a spring-mass system in simple harmonic motion is E = 1/2mω2A2. Suppose the oscillating particle is replaced by another particle of double the mass while the amplitude A remains the same. The new mechanical energy will
A body describes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 5 cm, and a period of 0.2 s. Find the acceleration and velocity of the body when the displacement is 3 cm, and when the displacement is zero.
A particle of mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion between points x1 and x2, the equilibrium position being O. Its potential energy is plotted. It will be as given below in the graph
Two simple harmonic motions of angular frequency 100 and 1000 rad s–1 have the same displacement amplitude. The ratio of their maximum acceleration is
The displacement of a particle along the x-axis is given by x = asin2ωt. The motion of the particle corresponds to
A body is vibrating in simple harmonic motion. If its acceleration is 12 cm s−2 at a displacement 3 cm, then time period is
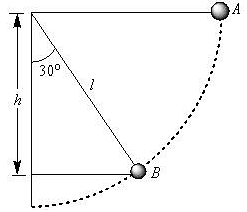
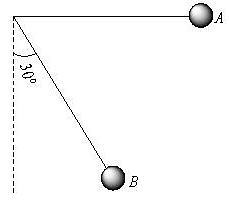
A simple pendulum is released from A shown.
If m and l represent the mass of the bob and Length of the pendulum, the gain kinetic energy at B is
For Simple Harmonic Oscillator, the potential energy is equal to kinetic energy
A particle is vibrating in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 4 cm. At what displacement from the equilibrium position is its energy half potential and half kinetic?
If the initial tension on a stretched string is doubled, then the ratio of the initial and final speeds of a transverse wave along the string is
In a guitar, two strings A and B made of same material are slightly out of tune and produce beats of frequency 6Hz. When tension in B is slightly decreased, the beat frequency increases to 7Hz. If the frequency of A is 530Hz, the original frequency of B will be
A tuning fork is used to produce resonance in a glass tube. The length of the air column in this tube can be adjusted by a variable piston. At room temperature of 27∘C two successive resonances are produced at 20cm and 73cm of column length. If the frequency of the tuning fork is 320Hz, the velocity of sound in air at 27∘C is
The two nearest harmonics of a tube closed at one end and open at other end are 220 Hz and 260 Hz. What is the fundamental frequency of the system?
The second overtone of an open organ pipe has the same frequency as the first overtone of a closed pipe L metre long. The length of the open pipe will be
|
1 videos|26 docs|111 tests
|