NEET Part Test - 6 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test NEET Mock Test Series 2025 - NEET Part Test - 6
Which level does natural selection operate on to evolve desired traits?
An age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is:
Interactions between different species living within a particular area may be:
Interacting members of species live close to each other in following interaction/s:
Which growth pattern occurs when resources become progressively limiting in a population?
Which measure indicates the inherent potential of a population to grow?
The rate of individuals born per 1,000 individuals per year is called
When the number of immigration and births is more than emigration and deaths, the growth curve of the population will show
If in a population, natality is balanced by mortality, then there will be
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
Given figure represents a pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem
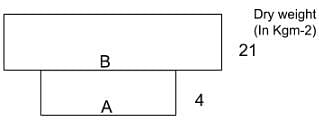
Identify A and B and select the correct answer.
(i) A is the crop which supports and B is the crop which is supported.
(ii) A is the crop which is supported and B is the crop which supports.
(iii) A is phytoplanktons and B is zooplanktons.
(iv) A is zooplanktons and B is phytoplanktons.
Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
In which of the following aspect do the components of the ecosystem are seen to function as a unit?
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as
What is an important reason for the conservation of natural resources?
Domesticated crop plants rarely become aggressive weeds, because
What are the species called whose number of individuals is greatly reduced recently and is decreasing continuously?
|
1 videos|26 docs|111 tests
|