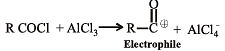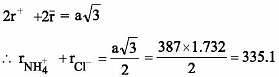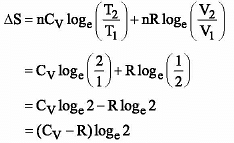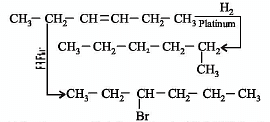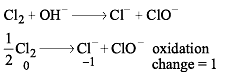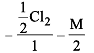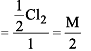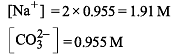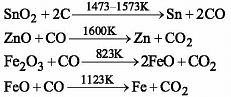NEET Practice Test - 18 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Practice Test - 18
In the Freidel Craft's acylation reaction, the effective electrophile is
Consider the following statements
I. The radius of an anion is larger than that of the parent atom.
II. The ionization energy generally increases with increasing atomic number in a period.
III. The electronegativity of an element is the tendency of an isolated atom to attract an electron.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
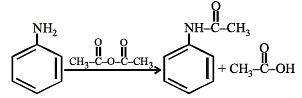
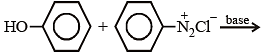
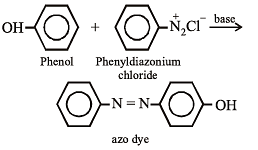
Aniline is an activated system for electrophilic substitution. The compound formed on heating aniline with acetic anhydride is
Which of the following can be repeatedly soften on heating?
(i) Polystyrene
(ii) Melamine
(iii) Polyesters
(iv) Polyethylene
(v) Neoprene
In which alkyl halide, SN2 mech an ism is favoured maximum ?
Which of the two ions from the list given below that have the geometry that is explained by the same hybridization of orbitals, NO2–, NO3–, NH2, NH4+, SCN– ?
NH4Cl crystallises in a bcc lattice with edge length of unit cell equal to 387 pm. If the radius of the Cl– ion is 181 pm, the radius of ![]() ions is
ions is
When one mole of an ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume and simultaneously heated to twice in initial temperature, the change in entropy (ΔS) is
For the reaction of one mole of zinc dust with one mole of sulphuric acid in a bomb calorimeter, ΔU and w corresponds to
In most cases, for a rise of 10K temperature the rate constant is doubled to tripled. This is due to the reason that
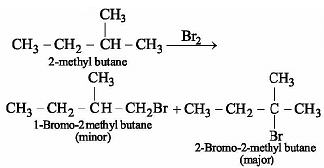
The major product obtained in the photo catalysed bromination of 2-methylbutane is:
In the presence of platinum catalyst, hydrocarbon A adds hydrogen to form n-hexane.
When hydrogen bromide is added to A instead of hydrogen, only a single bromo compound is formed. Which of the following is A?
An open beaker of water in equilibrium with water vapour is in a sealed container. When a few grams of glucose are added to the beaker of water, the rate at which water molecules :
Cl2 changes to Cl– and ClO– in cold NaOH. Equivalent weight of Cl2 will be
The formula mass of Mohr's salt is 392. The iron present in it is oxidised by KMnO4 in acid medium. The equivalent mass of Mohr's salt is
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption
Which of the following is used for making optical instruments?
25.3 g of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 is dissolved in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. If sodium carbonate dissociates completely, molar concentration of sodium ions, Na+ and carbonate ions, CO32– are respectively (Molar mass of Na2CO3 = 106 g mol–1)
Equilibrium constant K changes with temperature.
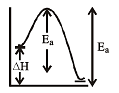
At 300 K, equilibrium constant is 25 and at 400 K it is 10. Hence, backward reaction will have energy of activation
The commonest method for the extraction of metals from oxide ores involves :
If x is amount of adsorbate and m is amount of adsorbent, which of the following relations is not related to adsorption process ?