JEE Advanced Practice Test- 6 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Advanced Practice Test- 6
The coefficient of linear expansion for a certain metal varies with absolute temperature as α = aT. If Lo = 1 m is the initial length of the metal and the temperature of metal is changed from 27oC to 127oC, then final length is (where a = 2 × 10-5 K−2)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
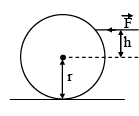
A billiard player hits a billiard ball of mass m and radius r lying at rest on the billiard table. When the cue hits the ball horizontally with force F at a height (r + h) from the table top the ball rolls without slipping. h is given as
A conducting rod is rotated by means of strings in a uniform magnetic field with constant angular velocity as shown in the figure. Potential of points A, B and C are VA, VB and VC respectively. Then
In the circuit shown (R = 1 Ω) current in branch CD is
A Π s haped wire frame with a light, smooth, sliding wire connected to its open end (width of open end is l) is dipped in a soap solution and then raised, such that a soap film forms between the slider and the closed end of the wire frame. If the wire frame is now placed in a vertical plane and a block of mass m is hung from the slider then for mass m to remain in equilibrium the surface tension of the soap film is
An artificial satellite of mass m is moving in a circular orbit at a height equal to the radius R of the Earth. Suddenly due to internal explosion the satellite breaks into two parts of equal masses. One part of the satellite stops just after the explosion and then falls to the surface of the Earth. The increase in the mechanical energy of the system (satellite + Earth) due to explosion will be (take acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth as g)
In position A kinetic energy of a particle is 60 J and potential energy is −20 J. In position B, kinetic energy is 100 J and potential energy is 40 J. Then in moving the particle from A to B
A metal rod is fixed in horizontal position and a force of magnitude F is applied as shown. If RA = force by wall A and RB = force by wall B, then
Two waves travelling in opposite directions produce a standing wave. The individual wave functions are given by y1 = 4 sin (3x – 2t) cm and y2 = 4 sin (3x + 2t) cm, where x and y are in centimeter. Now, select the correct statement(s) from the following.
A point source S is placed anywhere in between two converging mirrors having focal lengths f and 2f, respectively as shown. The value of d for which only single image may be formed is /are
In the circuit shown, initially keys K1, K2 and K3 are all open. Now certain events as described below are performed successively on the circuit which involve closing and opening of the keys K1, K2 and K3.
Event 1: Keys K1 and K2 are closed and K3 is left open.
Event 2: After a long time K2 is opened and K3 is closed.
Event 3: After a long time K1 is opened and K2 is closed.
Q.
The time constants for charging of capacitor (completion of Event 1) and rise of current through the inductor (completion of Event 2) respectively are
In the circuit shown, initially keys K1, K2 and K3 are all open. Now certain events as described below are performed successively on the circuit which involve closing and opening of the keys K1, K2 and K3.
Event 1: Keys K1 and K2 are closed and K3 is left open.
Event 2: After a long time K2 is opened and K3 is closed.
Event 3: After a long time K1 is opened and K2 is closed.
Q.
Find the maximum charge that can come on the capacitor after the completion of all the three events
In the circuit shown, initially keys K1, K2 and K3 are all open. Now certain events as described below are performed successively on the circuit which involve closing and opening of the keys K1, K2 and K3.
Event 1: Keys K1 and K2 are closed and K3 is left open.
Event 2: After a long time K2 is opened and K3 is closed.
Event 3: After a long time K1 is opened and K2 is closed.
Q.
Find the maximum current that can pass through the inductor after the completion of all the three events
A liquid flowing from a vertical pipe has a very definite shape as it flows from the pipe. To get the equation for this shape assume that the liquid is in free fall once it leaves the pipe. Just as it leaves the pipe, the liquid has speed vo and the radius of the cross section of the liquid stream is ro.
Q.
An equation for the speed v of the liquid as a function of the distance y it has fallen, is
A liquid flowing from a vertical pipe has a very definite shape as it flows from the pipe. To get the equation for this shape assume that the liquid is in free fall once it leaves the pipe. Just as it leaves the pipe, the liquid has speed vo and the radius of the cross section of the liquid stream is ro.
Q.
The expression for the radius of the cross-section of the liquid stream at a distance ‘y’ below the pipe is
The correct order of acidic strength of the compounds, 1 – 3 is
The mechanism involved in the following conversion is
The correct order of bond angle of the following compound is
The rate law for one of the mechanism of the pyrolysis of CH3CHO at 520oC and 0.2 bar is
The overall activation energy Ea in terms of rate law is:
The stopping potential (V0) of photosensitive surface varies with the frequency of incident radiation as shown in the following figure.
The work function of photosensitive surface.
5.6 litre of an unknown gas at NTP requires 12.5 calorie to raise its temperature by 10oC at constant volume.
The value of (PVm)P→0 of a real gas is independent of the nature of gas because
Which of the following oxide cannot be reduced by carbon reduction?
Which of the following can show both optical and geometrical isomeris?
Which of the following is (are) correct statement (s)?
Which of the following gives Cannizzaro’s reaction?
|
357 docs|148 tests
|
|
357 docs|148 tests
|

















