JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 3
The ratio of the energy of an X - ray photon of wavelength 1 Å to that of visible light of wave length 500 Å is
The de-Broglie wavelength associated with proton changes by 0.25% if its momentum is changed by P₀. The initial momentum was
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A fixed volume of iron is drawn into a wire of length l. The extension x produced in this wire by a constant force F is proportional to
What is the coefficient of mutual inductance, when the magnetic flux changes by 2X10-2 Wb and change in current is 0.01 A ?
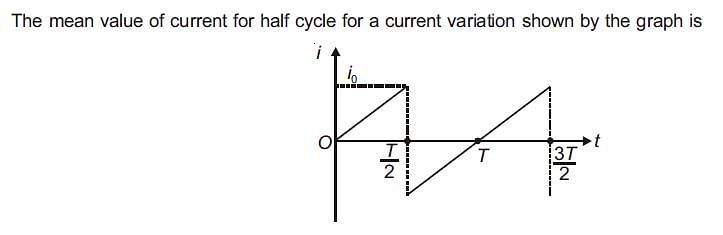
Vapour is injected at a uniform rate in a closed vessel which was initially evacuated. The pressure in the vessel
Condensers of capacities 2 μ F and 3 μ F are connected in series and a condenser of capacity 1 μ F is connected in parallel with them. The resultant capacity is
The electric potential V is given as a function of distance x (metre) by V = (5x2 + 10x - 9) volt. Value of electric field at x = 1m is
If 3.8 x 10-6 is added to 4.2 x 10-5 giving due regard to significant figures, then the result will be
The mass and diameter of a planet have twice the value of the corresponding parameters of earth. Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the planet is
Assertion(A): Pendulum of a clock is made of alloys and not of pure metals.
Reason(R): Use of alloys make the pendulum look good.
Assertion(A): Lifting of aircraft is caused by pressure difference brought by varying speed of air molecules.
Reason(R): As the wings/aerofoils move against the wind, the streamlines crowd more above them than below, causing higher velocity above than below.
The ratio of densities of nitrogen and oxygen is 14 : 16. The temperature at which the speed of sound in nitrogen will be same as that of oxygen at 55 oC is
The wavelength of ultrasonic waves in air is of the order of
Two rods of the same length and diameter having thermal conductivities K1 and K2 are joined in parallel. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the combination is
The Figure shows a rectangular loop of resistance R, width l and length a being pulled at a constant speed vthrough a region of thickness d(>a)d>a in which a uniform magnetic field of induction BB→ acting into the plane of paper is set up. The position of the loop at instant t is indicated by x, the distance penetrated by the right edge of the loop into the field with x = 0 at t = 0. (see diagram). Ignore the fringe effects on the magnetic field on the loop.
Q. If a graph is plotted for the flux φB through the loop as a function of the coil position x, which of the following will show the correct graph?
If a radioactive material is decayed by 29.28% in 10 minute, then its half life will be:-
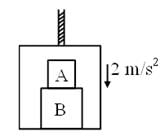
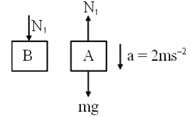
The elevator shown in figure is descending with an acceleration of 2 ms–2. The mass of the block A = 0.5 kg. The force exerted by the block A on the block B is 2x (take g = 10 ms–2). find the value of x.
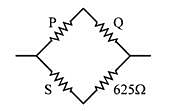
A Wheatstone's bridge is balanced with a resistance of 625 Ω in the third arm, where P, Q and S are in the 1st, 2nd and 4th arm respectively. If P and Q are interchanged, the resistance in the third arm has to be increased by 51Ω to secure balance. The unknown resistance in the fourth arm
If an objects is placed symmetrically between two plane mirrors, inclined at an angle of 72°, then the total number of images formed is:-
Two tuning forks A and B vibrating simultaneously produce 5 beats. Frequency of B is 512. It is seen that if one arm of A is filed, then the number of beats increases. Frequency of A will be:-
|
357 docs|148 tests
|
|
357 docs|148 tests
|


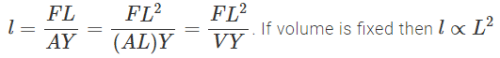

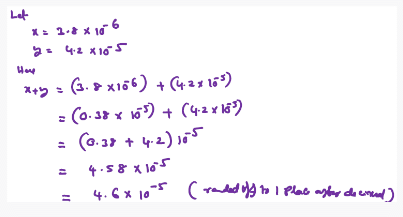
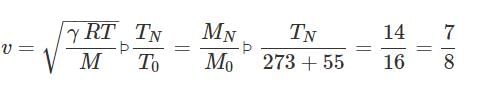 p p TN=287K=14∘C
p p TN=287K=14∘C

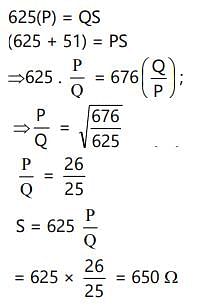
 ). Also it is given that beat frequency increases (i.e., x
). Also it is given that beat frequency increases (i.e., x )
) – nB = x
– nB = x = x
= x ...(ii) → Wrong
...(ii) → Wrong 














