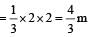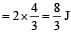31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 11 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 2
The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988]
A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of 1000 m/s and strikes the earth at the same level with a velocity of 500 m/s. The work done in joules overcoming the resistance of air will be[1989]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How much water, a pump of 2 kW can raise in one minute to a height of 10 m, take g = 10 m/s2? [1990]
Two identical balls A and B moving with velocities +0.5 m/s and –0.3 m/s respectively, collide head on elastically. The velocities of the balls A and B after collision, will be, respectively [1991]
A position dependent force, F = (7 – 2x + 3x2) N acts on a small body of mass 2 kg and displaces it from x = 0 to x = 5 m. Work done in joule is [1992]
Two masses of 1g and 9g are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their respective linear momenta is [1993]
Consider a car moving along a straight horizantal road with a speed of 72 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between road and tyres is 0.5, the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is[1994]
If the momentum of a body is increased by 50%, then the percentage increase in its kinetic energy is[1995]
The kinetic energy acquired by a mass (m) in travelling distance (s) starting from rest under the action of a constant force is directly proportional to [1994, 1996]
A body of mass m moving with velocity 3 km/h collides with a body of mass 2 m at rest. Now the coalesced mass starts to move with a velocity [1996]
Two bodies of masses m and 4 m ar e moving with equal K.E. The ratio of their linear momenta is[1997]
A molecule of mass m of an ideal gas collides with the wall of a vessel with a velocity v and returns back with the same velocity. The change in linear momentum of molecule is [1997]
A metal ball of mass 2 kg moving with a velocity of 36 km/h has a head on collision with a stationary ball of mass 3 kg. If after the collision, the two balls move together, the loss in kinetic energy due to collision is [1997]
Two equal masses m1 and m2 moving along the same straight line with velocities + 3 m/s and – 5m/s respectively, collide elastically.Their velocities after the collision will be respectively. [1998]
A force acts on a 30 gm particle in such a way that the position of the particle as a function of time is given by x = 3t – 4t2 + t3, where x is in metres and t is in seconds. The work done during the first 4 seconds is [1998]
A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 5m on a plane, where the acceleration due to gravity is not shown. On bouncing it rises to 1.8 m. The ball loses its velocity on bouncing by a factor of [1998]
Two bodies with kinetic energies in the r atio 4 : 1 are moving with equal linear momentum. The ratio of their masses is [1999]
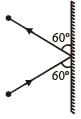
A 3 kg ball strikes a heavy rigid wall with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 60º. It gets reflected with the same speed and angle as shown here. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.20s, what is the average force exerted on the ball by the wall? [2000]
A bomb of mass 1 kg is thr own vertically upwards with a speed of 100 m/s. After 5 seconds it explodes into two fragments. One fragment of mass 400 gm is found to go down with a speed of 25 m/s. What will happen to the second fragment just after the explosion? (g = 10 m/s2) [2000]
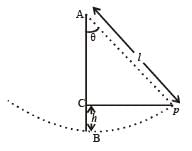
In a simple pendulum of length l the bob is pulled aside from its equilibrium position through an angle θ and then released. The bob passes through the equilibrium position with speed. [2000]
A force of 250 N is required to lift a 75 kg mass through a pulley system. In order to lift the mass through 3 m, the rope has to be pulled through 12m. Th e efficiency of system is [2001]
If the kinetic energy of a particle is increased by 300%, the momentum of the particle will increase by[2002]
When a long sprin g is stretched by 2 cm, its potential energy is U. If the spring is stretched by 10 cm, the potential energy stored in it will be[2003]
A stationary particle explodes into two particles of masses m1 and m2 which move in opposite directions with velocities v1 and v2. The ratio of their kinetic energies E1/E2 is [2003]
A mass of 0.5 kg moving with a speed of 1.5 m/ s on a horizontal smooth surface, collides with a nearly weightless spring of force constant k = 50 N/m. The maximum compression of the spring would be [2004]
A particle of mass m1 is moving with a velocity v1 and another particle of mass m2 is moving with a velocity v2. Both of them have the same momentum but their different kinetic energies are E1 and E2 respectively. If m1 > m2 then [2004]
A ball of mass 2 kg and another of mass 4 kg are dropped together from a 60 feet tall building.After a fall of 30 feet each towards earth, their respective kinetic energies will be in the ratio of [2004]
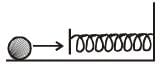
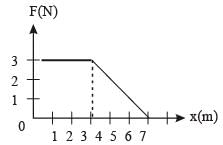
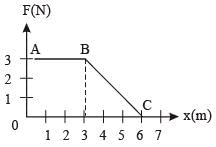
A force F acting on an object varies with distance x as shown here. The force is in N and x in m. The work done by the force in moving the object fr om x = 0 to x = 6 m is [2005]
A bomb of mass 30 kg at rest explodes into two pieces of masses 18 kg and 12 kg. The velocity of 18 kg mass is 6 ms–1. The kinetic energy of the other mass is [2005]
A body of mass 3 kg is under a constant force which causes a displacements in metres in it, given by the relation 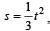 , where t is in seconds.
, where t is in seconds.
Work done by the force in 2 seconds is [2006]
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|


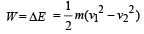
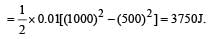
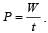 Here, P = 2kW = 2000 W..
Here, P = 2kW = 2000 W..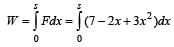
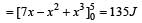
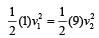
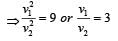
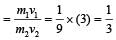
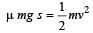
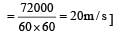
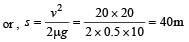
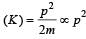
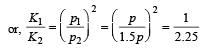
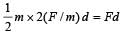
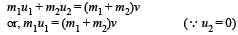
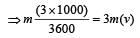
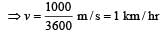
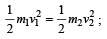
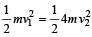
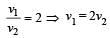

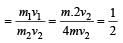
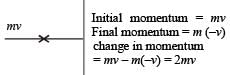
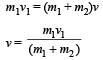
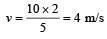
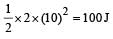
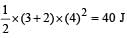
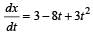
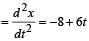
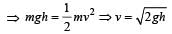
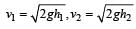
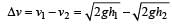
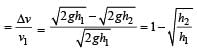
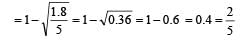
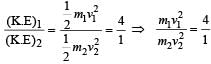
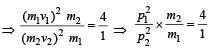
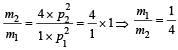
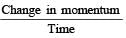
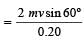
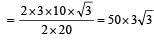
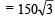 newton
newton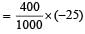 [downward]
[downward]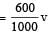
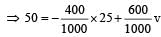
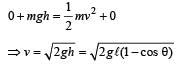
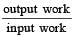
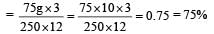
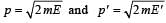
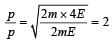
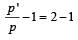
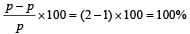
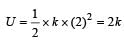
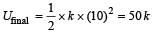
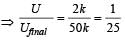
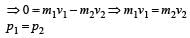
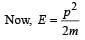
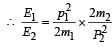
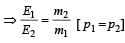
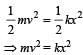
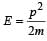
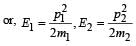
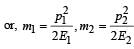
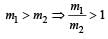
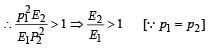
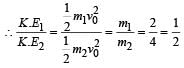
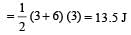
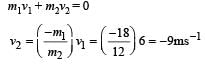
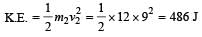
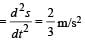
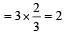 newton
newton