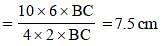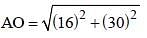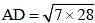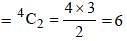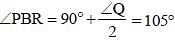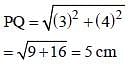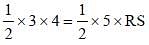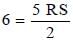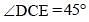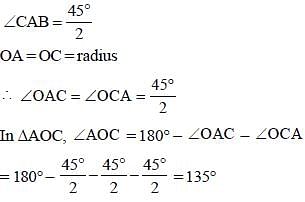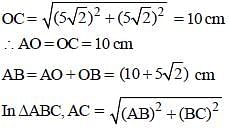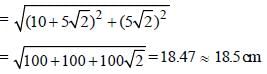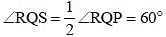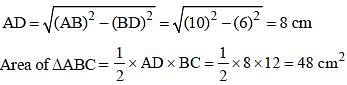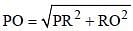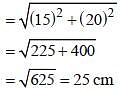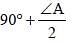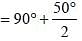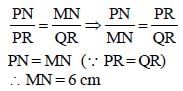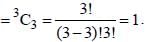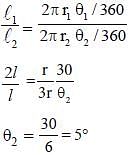SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 2 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Mathematics Previous Year Paper (Topic-wise) - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 2
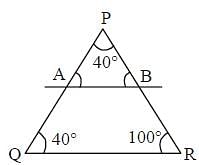
In ΔPQR, ∠P : ∠Q : ∠R = 2 : 2 : 5. A line parallel to QR is drawn which touches PQ and PR at A and B respectively.What is the value of ∠PBA - ∠PAB? (SSC Sub. Ins. 2017)
Find the sum of interior angles of a dodecagon? (SSC CHSL 2017)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
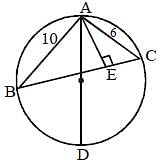
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which, AB = 10 cm, AC = 6 cm and altitude AE = 4 cm. If AD is the diameter of the circum-circle, then what is the length (in cm) of circumradius? (SSC CGL 2017)

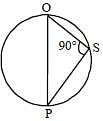
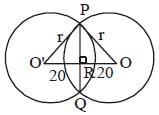
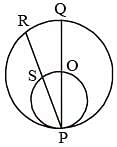
In the given figure, a smaller circle touches a larger circle at P and passes through its centre O. PR is a chord of length 34 cm, then what is the length (in cm) of PS? (SSC CGL 2017)
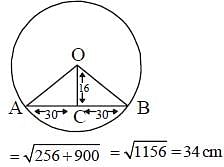
A chord of length 60 cm is at a distance of 16 cm from the centre of a circle. What is the radius (in cm) of the circle? (SSC CGL 2017)
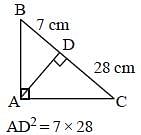
In ΔABC, ∠BAC = 90° an d AD is drawn perpendicular to BC. If BD = 7 cm and CD = 28 cm, then what is the length (in cm) of AD? (SSC CGL 2017)
If there are four lines in a plane, then what cannot be the number of points of intersection of these lines? (SSC CGL 2017)
In triangle PQR, A is the point of intersection of all the altitudes and B is the point of intersection of all the angle bisectors of the triangle. If ∠PBR = 105°, then what is the value of ∠PAR (in degrees)? (SSC CGL 2017)
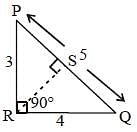
PQR is a right angled triangle in which ∠R = 90°. If RS ⊥ PQ, PR = 3 cm and RQ = 4 cm, then what is the value of RS (in cm)? (SSC CGL 2017)
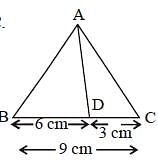
In triangle ABC, a line is drawn from the vertex A to a point D on BC. If BC = 9 cm and DC = 3 cm, then what is the ratio of the areas of triangle ABD and triangle ADC respectively? (SSC CGL 2017)
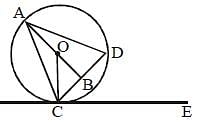
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle and ∠DCE = 45°. If CD = 10√2 cm, then what is the length (in cm) of AC. (CB = BD): (SSC CGL 2017)
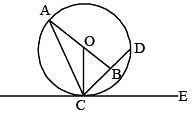
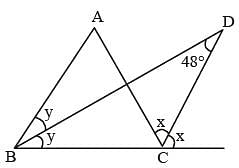
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. The bisectors of internal ∠B and external ∠C intersect at D. If ∠BDC = 48°, then what is the value (in degrees) of ∠A? (SSC CGL 2017)
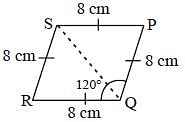
If length of each side of a rhombus PQRS is 8 cm and ∠PQR = 120°, then what is the length (in cm) of QS? (SSC CGL 2017)
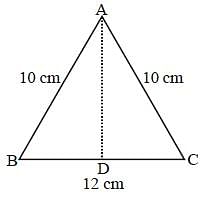
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 32 cm and each of the equal sides is 5/6 times of the base. What is the area (in cm2) of the triangle? (SSC CGL 2017)
In ΔPQR, ∠R = 54°, the perpendicular bisector of PQ at S meets QR at T. If ∠TPR = 46°, then what is the value (in degrees) of ∠PQR? (SSC CGL 2017)
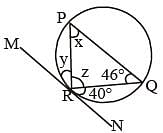
In the given figure, ∠QRN = 40°, ∠PQR = 46° and MN is a tangent at R. What is the value (in degrees) of x, y and z respectively? (SSC CGL 2017)
Two circles of same radius intersect each other at P and Q. If the length of the common chord is 30 cm and distance between the centres of the two circles is 40 cm, then what is the radius (in cm) of the circles? (SSC CGL 2017)
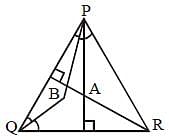
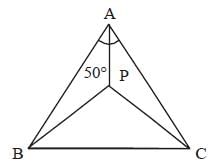
In the triangle ABC, ∠BAC = 50° and the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB meets at P. What is the value (in degrees) of ∠BPC? (SSC CGL 2017)
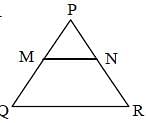
PQR is an equilateral triangle. MN is drawn parallel to QR such that M is on PQ and N is on PR. If PN = 6 cm, then the length of MN is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
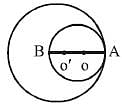
Two circles touch each other in ternally. The r adius of the smaller circle is 6 cm and the distance between the centre of two circles is 3 cm. The radius of the larger circle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
Number of circles that can be drawn through three noncolinear points is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
Which of the following ratios can be the ratio of the sides of a right angled triangle? (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
An arc of 30° in one circle is double an arc in a second circle, the radius of which is three times the radius of the first. Then the angles subtended by the arc of the second circle at its centre is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
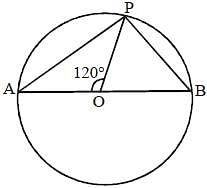
AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O and P be a point on its circumference, If ∠POA = 120°, then the value of ∠PBO is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
Which of the set of three sides can't form a triangle? (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
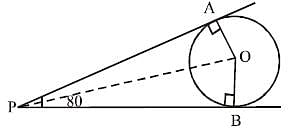
If PA and PB are two tangents to a cirlce with centre O such that ∠APB = 80°. Then, ∠AOP =? (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
In a triangle ABC, if ∠A + ∠C = 140° and ∠A + 3∠B = 180°, then ∠A is equal to (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
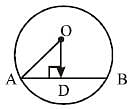
The length of the radius of a circle with centre O is 5 cm and the length of the chord AB is 8 cm. The distance of the chord AB from the point O is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
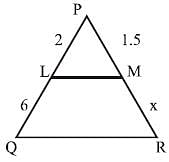
In ΔPQR, L and M are two points on the sides PQ and PR respectively such that LM II QR. If PL = 2cm; LQ = 6cm and PM = 1.5 cm, then MR (in cm) is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
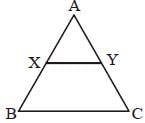
X and Y are the mid points of sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC. If BC + XY = 12 units, then BC – XY is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
|
21 docs|55 tests
|
|
21 docs|55 tests
|