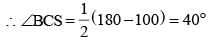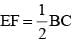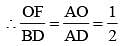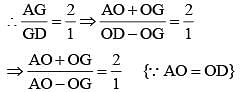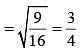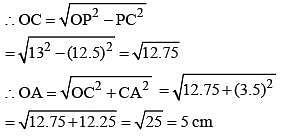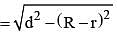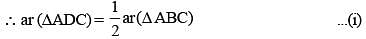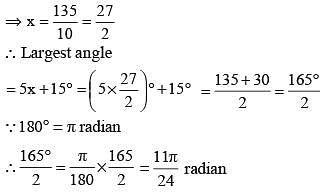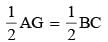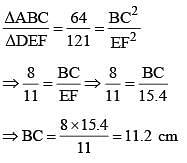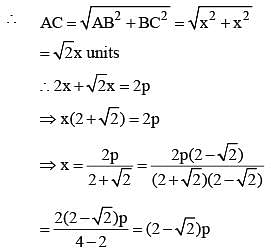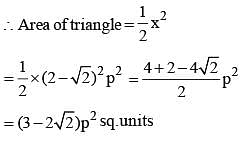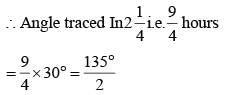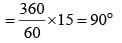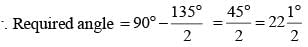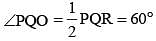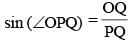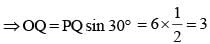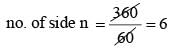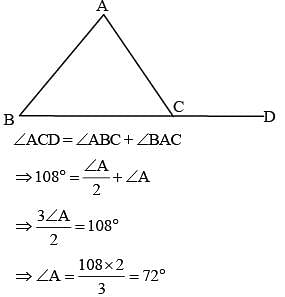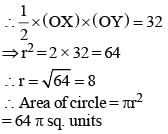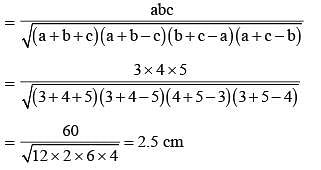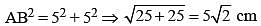SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 6 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Mathematics Previous Year Paper (Topic-wise) - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 6
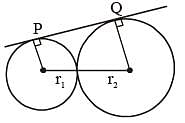
PQ is a direct common tangent of two circles of radii r1 and r2 touching each other externally at A. Then the value of PQ2 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
AC and BC are two equal chords of a circle. BA is produced to any point P and CP, when joined cuts the circle at T. Then (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
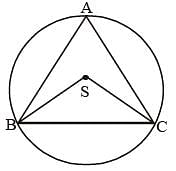
If S is the circumcentre of ΔABC and ∠A = 50°, then the value of ∠BCS is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
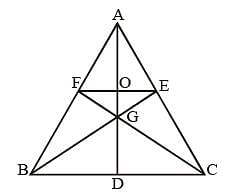
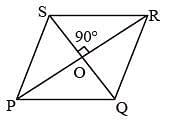
Let BE and CF the two median s of a ΔABC and G be their intersection. Also let EF cut AG at O. Then AO: OG is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is 9 : 16, then the ratio of their corresponding sides is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
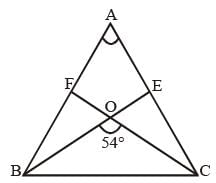
In an obtuse-angled triangle ABC, ∠A is the obtuse angle and O is the orthocenter. If ∠BOC = 54°, then ∠BAC is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
The perimeters of two similar triangle ΔABC and ΔPQR are 36 cm and 24 cm respectively. If PQ = 10 cm, then AB is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
P is a point outside a circle and is 13 cm away from its centre. A secant drawn from the point P intersect the circle at points A and B in such a way that PA = 9 cm and AB = 7 cm. The radius of the circle is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
R and r are the radius of two circles (R > r). If the distance between the centre of the two circles be d, then length of common tangent of two circles is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
AB is a diameter of a circle with centre O. CD is a chord equal to the radius of the circle. AC and BD are produced to meet at P. Then the measure of ∠APB is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
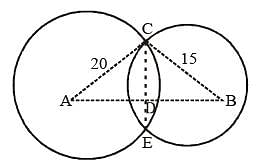
The length of the common chord of two circles of radii 15 cm and 20 cm whose centres are 25 cm apart is (in cm): (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
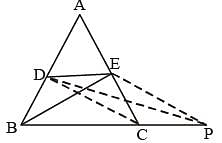
D and E are the mid-points of AB and AC of DABC; BC is produced to any point P; DE, DP and EP are joined. Then, (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
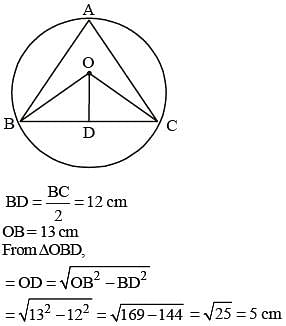
O is the circumcentre of the triangle ABC with circumradius 13 cm. Let BC = 24 cm and OD is perpendicular to BC. Then the length of OD is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
By decreasing 15° of each an gle of a trian gle, the ratios of their angles are 2 : 3 : 5. The radian measure of greatest angle is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
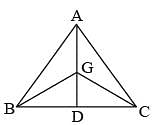
If G is the centroid of ΔABC and AG = BC, then ∠BGC is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
ΔABC and ΔDEF are similar and their areas be respectively 64 cm2 and 121 cm2. If EF = 15.4 cm, BC is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
The perimeter of an isosceles, right-angled triangle is 2p unit. The area of the same triangle is: (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
In ΔABC, AD is the median and AD = 1/2 BC. If ∠BAD = 30°, then measure of ∠ACB is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
Two sides of a triangle are of length 4 cm and 10 cm. If the length of the third side is 'a' cm. then (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
The angle formed by the hour–hand and the minute–hand of a clock at 2 : 15 p.m. is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If the length of the side PQ of the rhombus PQRS is 6 cm and ∠PQR = 120°, then the length of QS, in cm, is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If each interior angle is double of each exterior angle of a regular polygon with n sides, then the value of n is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
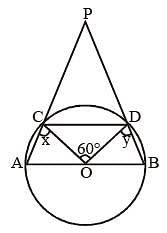
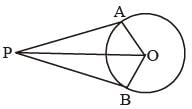
Two tangents are drawn from a point P to a circle at A and B. O is the centre of the circle. If ∠AOP = 60°, then ∠APB is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
Two circles of radii 4 cm and 9 cm respectively touch each other externally at a point and a common tangent touches them at the points P and Q respectively. They the area of a square with one side PQ, is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
The side BC of ΔABC is produced to D. If ∠ACD = 108° and 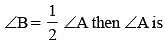 (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
(SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
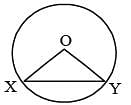
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle and XO is perpendicular to OY. If the area of the triangle XOY is 32, then the area of the circle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
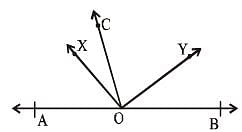
A, O, B are three points on a line segment and C is a point not lying on AOB. If ∠AOC = 40° and OX, OY are the internal and external bisectors of ∠AOC respectively, then ∠BOY is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
The length of radius of a circumcircle of a triangle having sides 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm is: (SSC CHSL 2012)
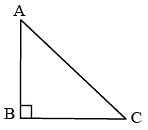
The length of the two sides forming the right angle of a right-angled triangle are 6 cm and 8 cm. The length of its circumradius is: (SSC CHSL 2012)
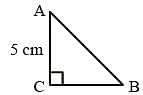
If ΔABC is an isosceles triangle with ∠C = 90º and AC = 5 cm, then AB is: (SSC CHSL 2012)
|
21 docs|55 tests
|
|
21 docs|55 tests
|