UGC NET Paper 2 Commerce Mock Test - 9 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Commerce Mock Test - 9
What is the sustainable growth rate of the company that enjoys return on equity = 30 percent and a dividend payout ratio of 40 percent?
Holistic marketers achieve profitable growth by expending customer share, ______, and capturing customer lifetime value.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Goods and Service tax came into effect from?
Which of the following incomes are exempt from tax?
1. Dividend received from the foreign company.
2. Agricultural income.
3. Remuneration received by an individual who is not a citizen of India
4. Long term Capital gain income (Below 1 lakh).
5. Dividend received from an Indian company.
6. Rental income of house property.
Codes:
Which kind of consumer behavior is spotted when there is significant differences between brands and also there is high involvement?
The Right to Information Act, 2005 makes the provision of _________________.
In most countries with income taxation, corporate entities are subject to tax on their profits and, in addition, are taxed in the hands of shareholders is known as ___________.
Direction: Read the statements carefully and choose the correct answer.
Statements: (I): The greater is the likely level of EBIT than the financial indifference point, the stronger is the case for issuing levered financial plans to maximise the EPS.
Statements(II): The financial break-even point is found at that level of EBIT where the EPS is zero for a particular financial plan.
If the sales are Rs. 6000, variable cost is Rs. 3600, and the fixed cost is Rs. 2000 then the break-even point will be -
European Union (EU) organization has its own governing and decision making institutions. Which one of the following is not associated with the EU organization?
Financial management is concerned with the:
What is the rate of the consumer price inflation for the first half of the current fiscal year?
Which of the following is not a method of forecasting demand?
Assertion (A): “Price Discovery” is a function of derivatives market.
Reason (R): ‘Price Discovery’ deals with the study of influence of futures price on spot price.
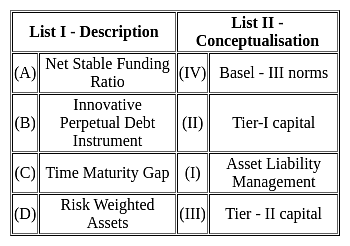
Match List I with List II:
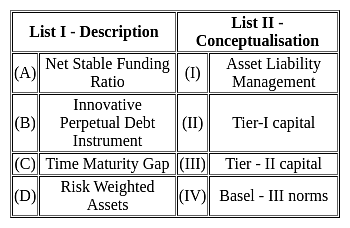
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
As per Section 68 of the Companies Act 2013, companies may purchase their own shares of which of the following?
A. its free reserves
B. the securities premium account
C. Net profits of the firm
D. The proceeds of the issue of any shares or other specified securities
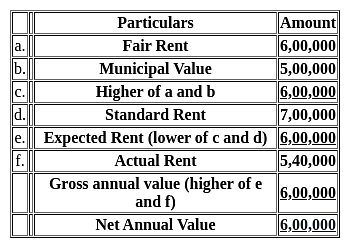
Which one of the following is the Net Annual Value (NAV) of house for the given details?
Municipal value = Rs. 5,00,000
Fair Rental value = Rs. 6,00,000
Standard Rent = Rs. 7,00,000
Actual Rent (Annual Rent) = Rs. 5,40,000
Municipal Tax = Rs. 15,000 (due but not paid)
For a hypothesis test, alpha (α) is 0.05 and beta (β) is 0.10. The power of this test is ________.
In the contract of agency, Implied agency may arise by:
A. Agency by Estoppel
B. Agency of Necessity
C. Agency by Ratification
D. Agency by Holding out
As per the RBI Act, 1934, the following functions are described as the functions of a Central Bank:
(i) Banking functions
(ii) Advisory functions
(iii) Supervisory functions
(iv) Promotional functions
Identify the correct combination:
In 'job evaluation', the key jobs are designated as ones:
The budgets are classified on the basis of:
|
16 docs|120 tests
|


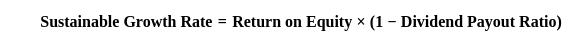


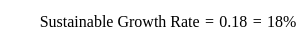

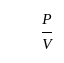 ratio
ratio 
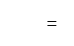 Sales
Sales  Variable cost
Variable cost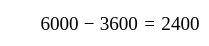
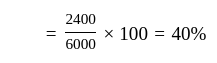
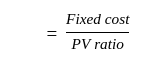
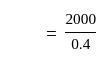
 Rs. 5000
Rs. 5000