UGC NET Paper 2 Education Mock Test - 9 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Education Mock Test - 9
Which one of the following focusses on transformation of the student from passive recipient of information to an active participant in the learning process?
In terms of Shewhart cycle, Set – I gives its stages, while Set-II specifies related actions:
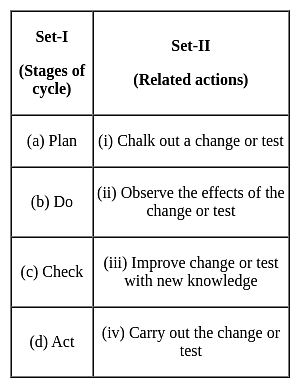
Match the two sets and indicate your answer from the options given below
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
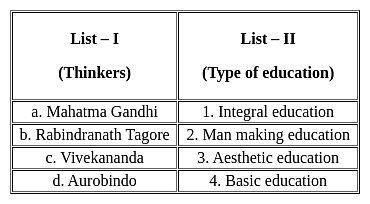
Match List – I with List – II in the following.

Which exponent is associated with the understanding level of teaching?
Assertion A): A teacher pairs a child who is very active with someone who is less active and clearly establishes the goal that what exact activity the pair would do.
Reason R): Peer tutoring is used in an inclusive classroom as it boosts the confidence of special children while learning with normal children.
Choose the correct answer from the following code:
What does some books are to be tasted mean?
How must we approach the 'meaner' sort of books?
_________ education is the belief that schooling needs to be solidly grounded in democratic values of associated living.
What are some challenges to implementing inclusive education in schools?
I. Lack of resources and support from the school administration
II. Collect some special need students' data.
The following statements are either True or False. Choose the correct statement(s) from the codes given below :
The scale on which the distance between scale positions are equal is :
(a) Ordinal Scale.
(b) Nominal Scale.
(c) Ratio Scale.
(d) Interval Scale.
Which of the following come under the mandate of the University Grants Commission (UGC)?
(A) Promotion and coordination of University education.
(B) Determining and monitoring standards of teaching, examination, and research in Universities.
(C) Organising continuous professional development programs for college and University teachers.
(D) Framing regulations on minimum standards of education.
(E) Disbursing and regulating grants to the universities and colleges.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
What do knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation belong to?
The most important trait of philosophy is
Which among the following does not fit into the scheme of educational goals of the Idealists?
Who said that the school be made as miniature society?
Assertion (A): The research hypothesis being the alternative hypothesis (H1) has to be kept in the domain of acceptability.
Reason (R): The Null hypothesis (H0) has been rejected at high alpha (significance) level thereby rendering the possibility of Type I error quite insubstantial.
Kindergarten (KG)system of education is indebted to
Which of the following set of statements appropriately differentiates between classical and operant conditioning paradigm?
(i) Classical conditioning involves stimulus-stimulus substitution whereas operant conditioning is S-R conditioning where S is made contingent on R.
(ii) Classical conditioning is related to psycho-somatic behaviour while operant conditioning deals with reflexes.
(iii) In classical conditioning reinforcement precedes a response while in operant conditioning it follows a response.
(iv) Subject is relatively active in classical conditioning whereas it is a passive responder in operant conditioning.
(v) The association between two stimuli is a critical factor in learning through classical conditioning while the response and reinforcement contingency is important for learning in operant conditioning.
Value conflicts in the minds of school children are often created by
|
16 docs|120 tests
|