UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 3 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 3
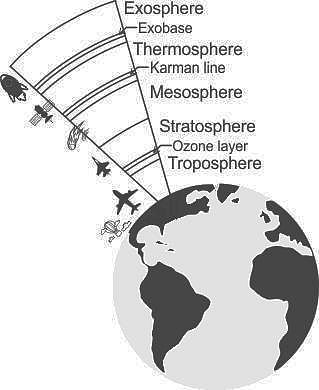
Which of these layers of the atmosphere is composed of the ozone layer which is responsible for absorbing ultraviolet (UV) light?
Western disturbances are extratropical storms that bring sudden winter rain to the northern parts of India. They originate in ______.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Carbon dioxide contributes in trapping the heat radiated from the earth. It is known called
Study the following pairs (P, Q, R, S) with respect to GPS receivers used in GPS surveys and select the correct answer based on the matching.
P : GPS receivers : L-band radio processor
Q : Self-contained GPS receivers : Also known as 'GPS mice'
R : Dual-frequency receivers : Survey grade GPS, position accuracy according to differential correction within sub-centimetre
S : Carrier phase receivers : GPS receivers with 10 to 30 cm position accuracy with differential correction
The following item consists of two statements, statement I and statement II. Examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answer from the code given below.
Statement I:
Summer is the favourable season for lumbering activity.
Statement II:
The Siberian region has a thriving lumbering industry.
Who among the following is known as the '‘father of exceptionalism’?
Which type of settlement pattern is having the following features?
1. narrow meandering streets and lanes
2. high population density
3. the high degree of nucleation
4. most common in India
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements:
1. Culture adapted to the dictates of Nature.
2. Culture is determined by Social Conditions.
Which of the above statement(s) is correct about Determinism?The dust and ash material hurled from the volcanoes are termed as:
In which layer the maximum part of the atmosphere (by mass) is found?
Which of the following is true about Tropical Rain forest?
(A) These forest are called evergreen forests.
(B) The trees in these forests shed their leaves at different times of the year.
(C) Sal, Teak and Shisham are important trees of these forests.
(D) These forests are called monsoon forests.
Choose the correct option
Select the ocean currents related to the Indian Ocean
Statement I: The Doldrums is a low-pressure area around the Equator where the prevailing winds are calm
Statement II: Low pressure is caused by the heat at the Equator which makes the air rise and travel both Northwards and Southwards
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion(A)- Standard Deviation is superior than the other measures of dispersion.
Reason(R)- It possesses almost all the requisites of a good measure of dispersion.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Development in ICT has led to increase in technical field of education in India.
Reason (R) : There has been increase in investment in ICT sector in India.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
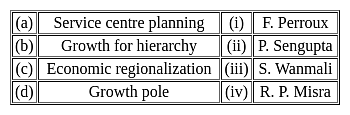
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below :
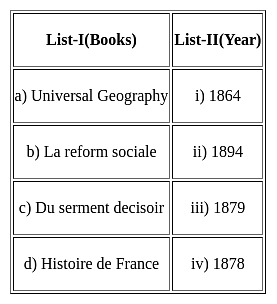
Choose the correct options from the following:
The winds that blow from the sea contain …………….. moisture
The_____ may be defined as the representation of the earth's pattern as a whole or a part of it
|
16 docs|120 tests
|