UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 7 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 7
Which one of the following indices is used to indicate if the optimal location was closer to either raw material source or the market?
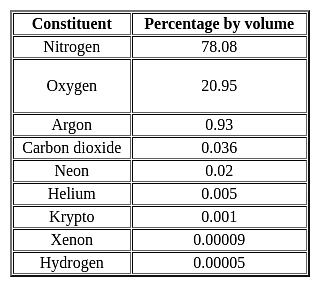
Major constituent gasses of the atmosphere are _____________.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
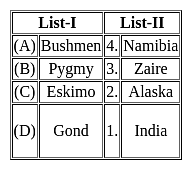
Match the list one with list two.
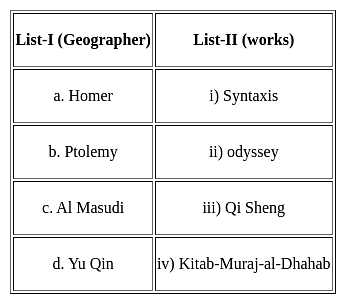
Choose the correct option from below :

Identify the INCORRECT statement(s) (S1, S2, S3) pertaining to the Vector data Model in GIS.
S1 : Topology is static and any updation /editing of vector data requires re-building of topology.
S2: Accurate geographic location of data can be maintained.
S3 : Continuous data like elevation data can be effectively represented in vector form.
Consider the following statements regarding Census-2011:
1. The percentage decadal growth of population during 2001-2011 has registered the sharpest decline since independence.
2. It created the National Population Register (NPR) which will build up a comprehensive identity database of usual residents of the country.
3. Census 2011 was conducted in two phases - the house listing phase and the population enumeration phase.
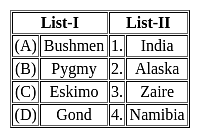
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Match List - I and List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below:
Which of the following statements relating to Ratzel's concept of Lebensraum, is not correct?
(a) It is the geographical area within which living organisms develop.
(b) It is the economic and cultural activity of the people outside their enclosed settled area.
(c). It deals with the relation between human society and a spatial organization and its physical setting.
(d). It is a geopolitical term that studies space from the viewpoint of the state.
Choose the correct option from below:
From the given processes below choose the processes involved in a water cycle.
A. Condensation
B. Insolation
C. Evaporation
D. Precipitation
Assertion(A)- Wegener was of the view that western and eastern coastlines of the Atlantic Ocean are in Jig-saw fit.
Reason(R)- The Continental drift theory was based primarily on two premises, which were polar wandering and matching of geological formations.
Choose the correct option:
Assertion(A)- The Sugar industry in southern regions of India is more productive.
Reason(R)- Sugar industry is gradual shifting from North India to the peninsular India.
Choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): The Puranas name the region of Madagascar and Eastern Africa as Shalmali.
Reason (R) : The region of East-Africa is rich in silk-cotton trees.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
At which among the following places, Brahamputra takes a U-turn at the time of entering into India?
Which of the following tribes is not found in Central India ?
The famous “Chatham Saw Mill” is located in which among the following states / union territories of India?
The average air pressure at the sea level is ……………… millibars
The difference between maximum and minimum temperature of the day is called …………..
|
16 docs|120 tests
|