Test: Enzyme Kinetics - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biochemistry for MCAT - Test: Enzyme Kinetics - 1
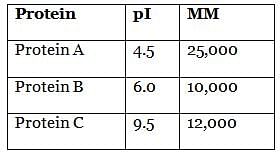
At what pH can protein A best be obtained through electrophoresis? (Note: MM = molar mass)

Which of the following is NOT involved in cell migration?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Hormones are found in the body in very low concentrations, but tend to have a strong effect. What type of receptor are hormones most likely to act on?
I. Ligand-gated ion channels
II. Enzyme-linked receptors
III. G protein-coupled receptors
I. Ligand-gated ion channels
II. Enzyme-linked receptors
III. G protein-coupled receptors
Which of the following characteristics is NOT attributed to antibodies?
Which of the following is NOT a component of all trimeric G proteins?
Which amino acids contribute most significantly to the pI of a protein?
I. Lysine
II. Glycine
III. Arginine
Which protein properties allow UV spectroscopy to be used as a method of determining concentration?
What property of protein-digesting enzymes allows for a sequence to be determined without fully degrading the protein?
What is the function of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in SDS-PAGE?
Which of the following proteins is most likely to be found extracellularly?
|
138 videos|21 docs|4 tests
|

















