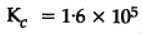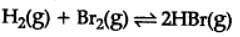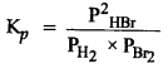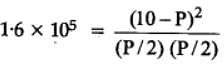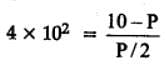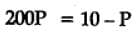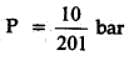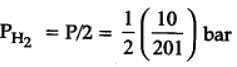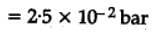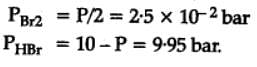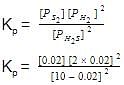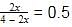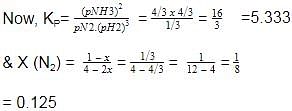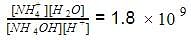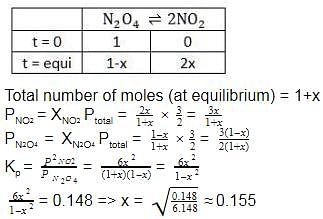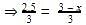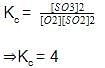Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Homogeneous Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Homogeneous Equilibrium
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Given the reactions, 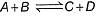 If one mole each of A and B are take in 5 L flask at 300 K, 0.7 mole of C are formed. Molar concentration of each species at equilibrium, when one mole of each are taken initially is
If one mole each of A and B are take in 5 L flask at 300 K, 0.7 mole of C are formed. Molar concentration of each species at equilibrium, when one mole of each are taken initially is

On taking 60.0 g CH3COOH and 46.0 g CH3CH2OH in a 5 L flask in the presence of H30+ (catalyst), at 298 K 44.0 g of CH3COOC2H5 is formed at equilibrium.
If amount of CH3COOH is doubled without affecting amount of CH3CH2OH, then CH3COOC2H5 formed is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the reversible reaction, 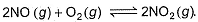
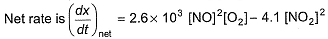
In a reaction vessel, [NO]= [O2]= 0.01 mol L-1 and [NO2]= 0.1 mol L-1 then above reaction is
In a reaction vessel, [NO]= [O2]= 0.01 mol L-1 and [NO2]= 0.1 mol L-1 then above reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction, is 1.6 x 105 at 1024 K.
H2(g) + Br2(g) ⇌2HBr(g)
HBr (g)at 10.0 bar is introduced into a sealed container at 1024 K. Thus, partial pressure of H2(g)and Br2(g), together is
At 273 K and 1 atm, 1 L of N2O4 (g) decomposes to NO2(g)a s given,
N2O4(g) ⇌2NO2(g)
At equilibrium, original volume is 25% less than the existing volume. Percentage decomposition of N2O4 (g) is thus,
H2S (g) initially at a pressure of 10.0 atm and a temperature of 800 K, dissociates as
2H2S(g) ⇌ 2H2(g) + S2(g)
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of S2 vapour is 0.020 atm . Thus, Kp is
A sample of N2O4(g)with a pressure of 1.00 atm is placed in a flask. When equilibrium is reached, 20% of N2O4(g)has been converted to NO2(g)
If the original pressure is made 10% of the earlier pressure, then per cent dissociation will be
Following equilibrium is set up at 1000 K and 1 bar in a 5 L flask,
At equilibrium, NO2 is 50% o f the total volume. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is
Following equilibrium is set up at 298 K in a 1 L flask.
If one starts with 2 moles of A and 1 mole of B, it is found that moles of B and D are equal.Thus Kc is
At 700 K and 350 bar, a 1 : 3 mixture of N2(g) and H2(g) reacts to form an equilibrium mixture containing X (NH3)= 0.50. Assuming ideal behaviour Kp for the equilibrium reaction,
Equilibrium constant for the reaction,
is 1.8 x 109. Hence, equilibrium constant for
A gaseous phase reaction taking place in 1L flask at 400 K is given,
Starting with 1 mole N2 and 3 moles H2, equilibrium mixture required 250 mL of 1M H2SO4 . Thus, Kc is
For the following equilibrium starting with 2 moles SO2 and 1 mole O2 in 1 L flask,
Equilibrium mixture required 0.4 mole in acidic medium. Hence, Kc is
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q. Statement I
If Kc = 4 for the following equilibrium,
Then mixture of 1 mole N2, 3 moles H2 and 2 moles NH3 in 1L flask is in equilibrium.
Statement II
Reaction quotient of the given quantities is less than the equilibrium constant.
Statement I
1 mole A(g) and 1 mole B(g)give 0.5 mole of C(g)and 0.5 mole D(g) at equilibrium.
On taking 2 moles each of A(g)and B(g), percentage dissociation A(g)and B(g) is also doubled.
Statement II
Equilibrium constant, Kc = 1
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-19) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
The equilibrium reaction has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 K
If the total pressure in a flask containing NO2 and N2O4 gas at 25°C is 1.50 atm, what fraction of the N2O4 has dissociated to NO2 ?
Passage I
The equilibrium reaction has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 K
Q. If the volume of the container is increased so that the total equilibrium pressure falls to 1.00 atm, then fraction of N2O4 dissociated is
Passage II
A 15 L flask at 300 K contains 64.4 g of a mixture of NO2 and N2O4 in equilibrium. Given,
Q. Kc for the above equilibrium is
Passage II
A 15 L flask at 300 K contains 64.4 g of a mixture of NO2 and N2O4 in equilibrium. Given,
Q. Total pressure in the flask is
Direction (Q. Nos. 20) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. In the following equilibrium, is set up at 298 K in a 5 L flask. Experiment is carried by taking 0.1 mole each of H2(g)and l2(g). After equilibrium is attained, l2(g)was dissolved in Kl and required 100 mL of 0.1 M Na2S2O3 solution.
Match the values given in Column II with the respective terms in Column I
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. For the equilibrium in gaseous phase in 2 L flask we start with 2 moles of SO2 and 1 mole of O2 at 3 atm,
When equilibrium is attained, pressure changes to 2.5 atm. Hence, equilibrium constant Kc is
|
129 videos|238 docs|88 tests
|