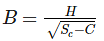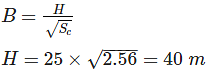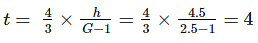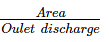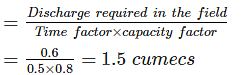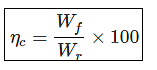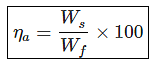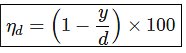Test: Irrigation Engineering- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Mock test series of SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 - Test: Irrigation Engineering- 2
Which of the following statement is correct for sprinkler irrigation method?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The Lacey’s silt factor for a particular alluvium is 2.0. This alluvium would comprise:
The base width of a solid gravity dam is 25 m. The material of the dam has a specific gravity of 2.56 and the dam is designed as an elementary profile ignoring uplift. What is the approximately allowable height of the dam?
At a certain point in the floor of weir, the uplift pressure head due to seepage is 4.5 m. If the relative density of concrete is 2.5, the minimum thickness of floor required at this point to counteract the uplift pressure is:
In a river, silt excluder and silt ejector are constructed:
The most economical method of soil conservation is to:
Outlet discharge for a particular crop is given by:
The loss of head per unit length of the creep is called:
Groynes are adopted for river bank protection works. When it is placed inclined downstream in the direction of flow in the river, it is designated as which one of the following?
If the discharge required for different crops is 0.6 cumecs in the field and the capacity factor and time factors are 0.8 and 0.5 respectively, then what is the design discharge of the distributary at its head?
If D is the depth of scour below original bed, then the width of launching apron is generally taken as:
The ratio of the water stored in the root zone during irrigation, to the water needed in the root zone prior to irrigation is called:
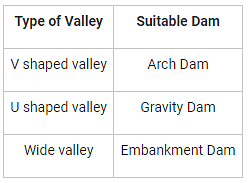
A constant centre (in plan – view) arch dam is best suited for:
|
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|
|
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|