Test: GOC, Aromaticity, Acidity & Basicity - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: GOC, Aromaticity, Acidity & Basicity - 1
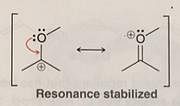
Which of the following is not a resonance structure of the others?
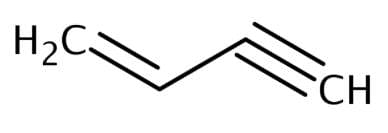
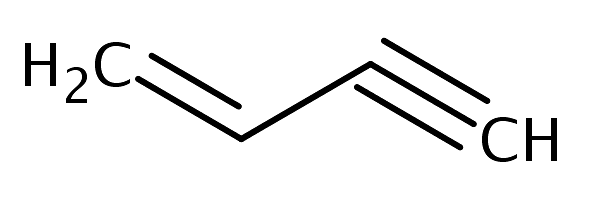
The number of sigma and pi-bonds in 1-butene 3-yne are:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following molecules has all the effects : inductive, mesomeric and Baker Nathan effect ?
Which one is strongest acid among following options?
Most stable resonating structure of the given carbocation is:
Which of the following resonance structures contributes the most to the resonance hybrid?
Stability order of the following resonating structure will be:
Hyperconjugation is best described as:
The correct stability order for the following species is:
Set the following in increasing order of their pKa values:
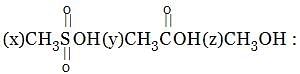
Identify order of per ring resonance energies of each of the following:
Identify the correct C-O bond length order:
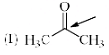
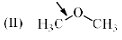
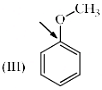
Which of the following systems are resonance contributors of the radical shown below?
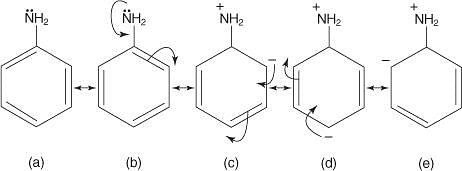
Which of the following statements about the resonance structures is false?
Which comparison is not correct as indicated?
In the following compounds,
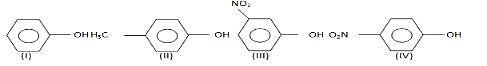
The order of acidity is
In the following compounds the order of acid strength is:
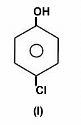
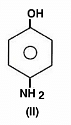
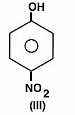
The acidity of protons H in each of the following is:
Identify the correct acidic strength order in the following compounds?
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds:


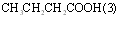
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|