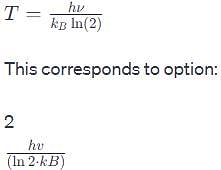Test: Molecular Spectroscopy - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Molecular Spectroscopy
The molecule which is IR-inactive but Raman–active is:
The rotational (microwave) spectrum of a rigid diatomic rotor consists of equally spaced lines with spacing equal to:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Upon application of a weak magnetic field, a line in the microwave absorption spectrum of rigid rotor splits into 3 lines. The quantum number (J) of the rotational energy level from which the transition originates is:
The vibrational frequency of a homonuclear diatomic molecule is v. The temperature at which the population of the first excited state will be half that of the ground state is given by.
The vibrational rotational spectrum is observed in …………….. region.
In a rotational spectrum, transitions are only observed between rotational levels of ΔJ =
Vibrational transitions are always accompanied by ………… transitions.
The increase in rotational energy shows absorption spectrum in.
The increase in vibrational energy leads to absorption spectrum in:
State which of the following molecules can show a pure rotational microwave spectrum:
Which of the following diatomic molecule will not give a rotation in spectrum:
The selection rule of the translation energy levels in the Raman spectrum is:
The population (N) distribution over states (n) of a diatomic molecule corresponds to:
The rotational spectrum of HI is found to contain a series of lines with a separation of 12.8 cm–1 . Moment of for the molecule is:
The bond length in CN+ is 0.129 nm. The position of second line in the microwave spectrum is:
Among the singlet (S), doublet (D) and triplet (T). electronic states, phosphorescence involves transition between:
For pure vibrational spectra, the selection rule is:
The Jmax for a rigid diatomic molecule for which at 300K, the rotational constant is 1.566 cm–1, is:
The inter nuclear distance for H35 Cl is 0.13 nm and the force constant is 500 Nm–1. The first excitat ion energy in cm–1 of H35 Cl molecule in the harmonic approximation is:
The fundamental vibration frequency and rotational constant of carbon monoxide molecule are 6.5 x 1013 s-1 and 1.743 x 1011 s-1 respectively. The rotational will have the same energy as ir would have in its first vibrational states with no rotational energy is:
Calculate the frequency at which the transition between the two spin states of a free electron may be observed at a field strength of 0.3000 T:
The different types of energies associated with a molecule are __________.
The pure rotational (microwave) spectrum of the gaseous molecule CN consists of a series of equally spaced line separated by 3.7978 cm–1. The inter nuclear distance of the molecule is [Molar masses are 12C=12.011 and 14N=14.007 g mol–1]:
Rotational quantum number for the rotational spectrum of diatomic molecule for maximum populated level is given by:
Which one of the following exhibits rotation spectra:
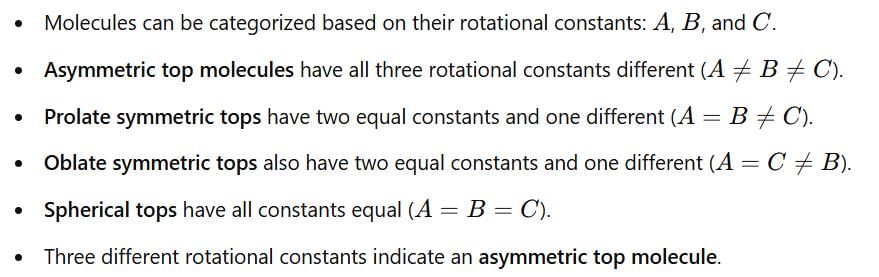
The microwave spectrum of a molecule yields three rotational constants. The molecule is:
The Q band in the vibrational spectrum of acetylene is observed in the:
Which of the following spectroscopic techniques will be useful to dist inguish between M–SCN and M–NCS binding modes:
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|