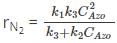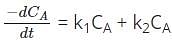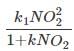Test: Steady State Approximation in Reaction Mechanisms - Chemistry MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Steady State Approximation in Reaction Mechanisms
In the formation of phosgene from carbon monoxide and chlorine, which of the following is rate determining?
At very low concentrations of azomethane, its decomposition follows which order?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The reaction involving oxidation of nitric oxide to nitrous oxide follows the mechanism ____
The rate determining step of a series of reactions is the one ____
Formation of hydrogen iodide from the corresponding elements is a ____
The order of the reaction involving the conversion of ozone to oxygen is ____
An assumption of Steady State Approximation is ____
For the parallel reaction A → B and A → C, of rate constants k1 and k2 respectively, both reactions of order 1, the rate expression is given as ____
State true or false.
Decomposition of nitrogen pentoxide follows second order mechanism, assuming that the kinetics is controlled by a single step mechanism.
State true or false.
Gas phase decomposition of N2O follows first order mechanism for low concentrations of N2O and second order mechanism for high concentrations of N2O.
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|