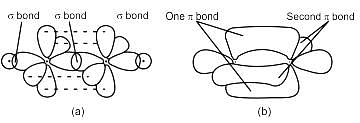
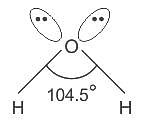
Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Tests > Inorganic Chemistry > Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Chemistry MCQ
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Chemistry MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Inorganic Chemistry - Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules for Chemistry 2024 is part of Inorganic Chemistry preparation. The Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus.The Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules MCQs are made for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules below.
Solutions of Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules questions in English are available as part of our Inorganic Chemistry for Chemistry & Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules solutions in
Hindi for Inorganic Chemistry course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules | 10 questions in 12 minutes | Mock test for Chemistry preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Inorganic Chemistry for Chemistry Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 1
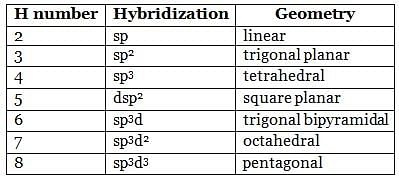
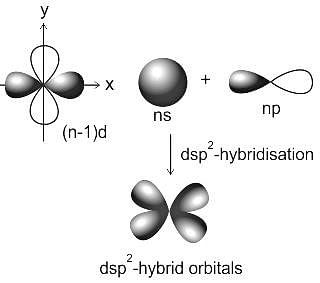
Square planar complex results from ___________ hybridization.
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 3
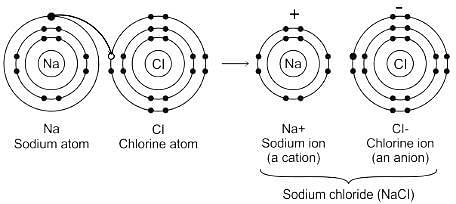
Which type of bond is present in NaCl molecule
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 3
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 4
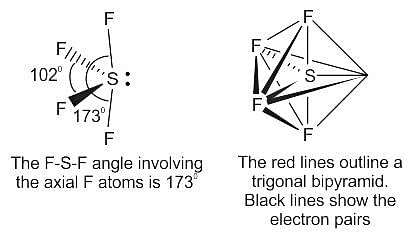
Which of the following has sp3d hybridization?
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 4
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 5
Pick out the isoelectronic structure from the Following:
I.CH3+, II.H3O+, III. NH3, IV. CH3-
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 5
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 6
The atomic number of magnesium is 12 and mass number is 24. Which one of the following is the correct representation of the ion formed from it and its valency?
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 6
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 7
The mode of hybridization of carbon in CO is
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 7
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 8
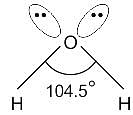
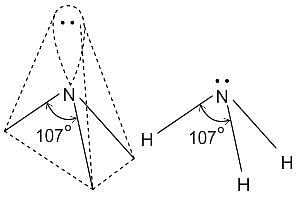
What is the hybridisation of the oxygen atom in water?
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 8
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 9
The shape a molecule occupies allows to minimize repulsions among them and maximize the space between them.
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 9
Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 10
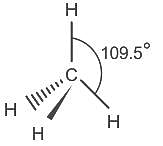
The VSEPR Model is used for predicting the ______________ of the molecules.
Detailed Solution for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules - Question 10
|
48 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
Information about Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: VSEPR Theory & shapes of molecules , EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice