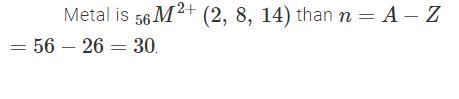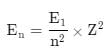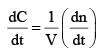Test: Gaseous State - 4 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Gaseous State - 4
Maximum number of electrons in a subshell with l = 3 and n = 4 is
Among the following curves, which is not according to Charle’s law:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The electronic configuration of a dipositive metal M2+ is 2, 8, 14 and its atomic weight is 56 a.m.u. The number of neutrons in its nuclei would be
The energy of an electron in first Bohr orbit of H-atom is –13.6 eV. The possible energy value of electron in the excited state of Li2+ is
Which of the following curve does not represent gay lusacc’s law:
For the gaseous reaction, the rate is often expressed in terms of dp/dt instead of dC/dt or dn/dt. (where c is the concentration and n the number of mol). What is the relationship among these three expression:
For a closed (not rigid) container containing n = 10 moles of an ideal gas fitted with a movable, frictionless, weightless piston operating such that pressure of gas remains constant at 0.821 atm, which graph represents the correct variation of log V vs log T where V is in litre and T in Kelvin:
At a definite temperature (T), the distribution of velocities is given by the curve. The curve that indicates that the velocity corresponding to points A, B and C are:
A graph is plotted between P (atm) vs t°C for 10 mol of an ideal gas as follows:
Then slope of curve and volume of container (L) respectively, is
For two samples A and B of ideal gas following curve is plotted between n vs V (volume) of container) at 16.42 atm pressure as follows, then temperature of A and B respectively are:
Match the correct from List-1 to List-2 on the basic of following Andrews isotherm of Real gas

Match the Colum –I and Column-II

Fraction of the gas particles
Initial temperature of an ideal gas is 75°C. At what temperature, the sample of neon gas would be heated to double its pressure, it the initial volume of gas is reduced by 15%:
At constant volume for a fixed number of moles of a gas, the pressure of the gas increases with the rise in temperature due to:
Three flasks of equal volumes contain CH4, CO2, and Cl2 gases respectively. They will contain equal number of molecules if:
At 0°C and one atm pressure, a gas occupied 100 cc. If the pressure is increased to one and a halftime and temperature is increased by one-third of absolute temperature, then final volume of the gas will be:
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|