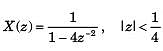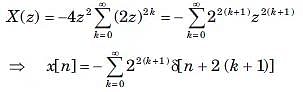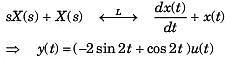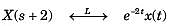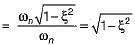Test: ESE Electrical - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Engineering Services Examination (ESE) Mock Test Series 2024 - Test: ESE Electrical - 1
For the circuit given below.
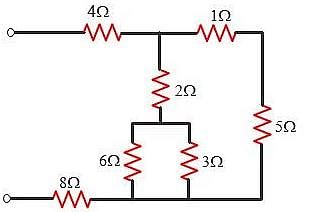
What is the value of equivalent resistance?

In the circuit given, a charge of 600 C is delivered to the 100 V source in a 1 minute. The value of v1 must be:


| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
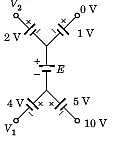
In the circuit of the fig the value of the voltage source E is:

In the case of a sinusoidal current, the unit of the amplitude is:
A sinusoid wave is expressed as 5 sin(4πt – 60°). Find the frequency.
What will be the period of the sinusoid, v(t) = 12 cos (50t + 30°)?
In a two element series circuit, the applied voltage and the resulting current are v(t) = 60 + 66sin (10 t) V, i(t) = 2.3sin (103t + 68.3o) A.The nature of the elements would be
In a balanced three-phase system-delta load, if we assume the line voltage is VRY = V∠0° as a reference phasor. Then the source voltage VYB is?
If the system is a three-wire system, the currents flowing towards the load in the three lines must add to ___ at any given instant.
Find the electric field intensity of transformer oil (εr = 2 approx) with density 1/4π (in 109units)
Electric flux density in electric field is referred to as
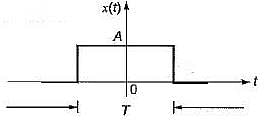
What is the total energy of the rectangular pulse shown in figure below?
Given the transform pair below. Determine the time signal y(t) and choose correct option.
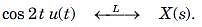
Y(s) = (s + 1)X(s)
Given the transform pair below. Determine the time signal y(t) and choose correct option.
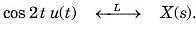
Y(s) = X(s + 2)
Consider a periodic signal x[n] with period N and FS coefficients X [k]. Determine the FS coefficients Y [k] of the signal y[n] given in question.
y[n] = x[n - no]
Consider a periodic signal x[n] with period N and FS coefficients X [k]. Determine the FS coefficients Y [k] of the signal y[n] given in question.
y[n] = x[n] + x[n + N/2] , (assume that N is even)
Determine the Fourier series coefficient for given periodic signal x(t).
x(t) as shown in fig.
The highest frequency component of a speech signal needed for telephonic communications is about 3.1 kHz. What is the suitable value for the sampling rate?
If X(k) is the DFT of x(n) which is defined as x(n)=x1(n)+jx2(n), 0≤ n≤ N-1, then what is the DFT of x1(n)?
Which of the following condition should the unit sample response of a FIR filter satisfy to have a linear phase?
Consider the following statements regarding control systems:
- In open loop control system, the control action depends upon the desired output.
- All control systems operated by present timing mechanism are open loop.
- In a closed loop control system feedback signal is usually negative.
- In open-loop control system stability cannot be ensured.
Which of the above statements are correct?
The transfer function of the control system represented by the block diagram shown below is

The ratio of damped frequency to natural frequency of the given system having damping ratio ξ is
The number of sign changes in the Routh’s array indicates the number of roots lying in the
Which of the following option is correct?
The root locus is the path of the roots of the characteristic equation traced out in the s-plane
The initial slope of Bode plot for a transfer function having no poles at origin is


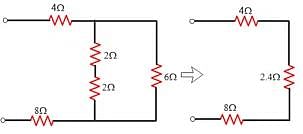
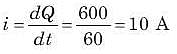




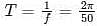


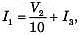 V2 = 4(I2 + I3) ⇒ I3 = 0.25V2 - I2
V2 = 4(I2 + I3) ⇒ I3 = 0.25V2 - I2