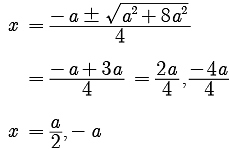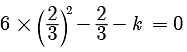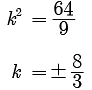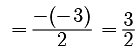Assertion & Reason Test: Quadratic Equations - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Quadratic Equations - 2
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The values of x are 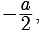 a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .
a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .
Reason : For quadratic equation ax2 + bx+ c = 0
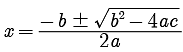
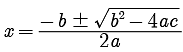
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The value of k = 2 , if one root of the quadratic equation 6x2 -x- k = 0 is ⅔
Reason : The quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 a has two roots.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : If roots of the equation x2 - bx + c = 0 are two consecutive integers, then b2 - 4c =1
Reason : If a, b, c are odd integer then the roots of the equation 4abc x2 + (b2 - 4ac)x - b = 0 are real and distinct.
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : A quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 , has two distinct real roots, if b2 - 4ac >0 .
Reason : A quadratic equation can never be solved by using method of completing the squares.
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : 4x2 -12x+9 =0 has repeated roots.
Reason : The quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 have repeated roots if discriminant D > 0 .
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : (2x - l)2 - 4x2 + 5 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
Reason : x = 0, 3 are the roots of the equation 2x2 -60x = 0.
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The equation 8x2 + 23kx+0 = has equal roots then the value of k is ![]()
Reason : The equation ax2 + bx+ c = 0 has equal roots if D =b2 - 4ac =0
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The roots of the quadratic equation x2 + 2x+2 = 0 are imaginary.
Reason : If discriminant D =b2 - 4ac <0 then the roots of quadratic equation ax2 + bx+ c = 0 are imaginary.
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The equation 9x2 + 34kx + 4 = 0 has equal roots for k = + 4 .
Reason : If discriminant ‘D’ of a quadratic equation is equal to zero then the roots of equation are real and equal.
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Sum and product of roots of 2x2 -35x+0 = are ![]() and
and![]() respectively.
respectively.
Reason : If a and b are the roots of ax2 + bx + c = 0 , a ≠ 0 , then sum of roots = α +β = ![]() and product of roots
and product of roots ![]()