DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 5 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test DSSSB PGT Mock Test Series 2024 - DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 5
What is the dimension of k/m where k is the force constant and m is the mass of the oscillating object?
A thin circular ring of mass m and radius R is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity w. Two objects each of mass M are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with an angular velocity w' =
[AIEEE 2006]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the given uniform square lamina ABCD, whose centre is O
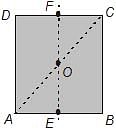
[AIEEE 2007]
Two point masses of mass 4m and m respectively separated by d distance are revolving under mutual force of attraction. Ratio of their kinetic energies will be
with the orbit radius of a body in circular planetary motion. Find the correct state ment about the
curves A, B and C
A satellite which appears to be at a fixed position at a definite height to an observer is called:
The process by which heat flows from the region of higher temperature to the region of lower temperature by actual movement of material particles is called
The ratio of the adiabatic to isothermal elasticities of a triatomic gas is
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is at an initial temperature of 300 K. The gas undergoes an isovolumetric process, acquiring 500 J of energy by heat. It then undergoes an isobaric process, losing this same amount of energy by heat. Determine the work done on the gas.
A particle of mass m is allowed to oscillate on a smooth parabola x2 = 4ay, a > 0, about the origin O (see figure). For small oscillations, find the angular frequency ( ω )
If the path difference between the interfering waves is nl, then the fringes obtained on the screen will be
A point charge causes an electric flux of −1.0×103Nm2/C to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on the charge.
(a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface?
(b) What is the value of the point charge?
Under the influence of the coulomb field of charge +Q, a charge −q is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement(s).
A point charge causes an electric flux of −1.0×103 Nm2/C to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centered on the charge.
(a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface?
(b) What is the value of the point charge?
A point charge 2nC is located at origin. What is the potential at (1,0,0)?
It is necessary to use satellites for long distance TV transmission because
The Brewster’s angle for a transparent medium is 600.The angle of incidence is
Number of ejected photoelectrons increases with increase
Reason why there are many lines in an atomic spectrum is because
90% of a radioactive sample is left undisintegrated after time τ has elapsed, what percentage of initial sample will decay in a total time 2τ?
The depletion layer in the p-n junction is caused
How many depletion regions does a transistor have?
A fixed volume of iron is drawn into a wire of length l. The extension x produced in this wire by a constant force F is proportional to
The ratio of densities of nitrogen and oxygen is 14 : 16. The temperature at which the speed of sound in nitrogen will be same as that of oxygen at 55 oC is


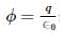 since amount of charge not depends on size and shape so by making radius < double the amount of charge remain same so electric flux remain same.
since amount of charge not depends on size and shape so by making radius < double the amount of charge remain same so electric flux remain same.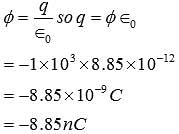
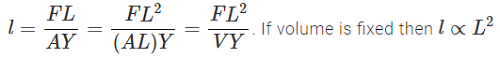
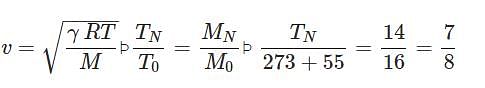 p p TN=287K=14∘C
p p TN=287K=14∘C















